The dosage of solid calcium hypochlorite Ca(ClO)2 it's easier …
… because it contains a higher proportion of free chlorine and does not disintegrate under favorable conditions. Calcium hypochlorite is the calcium salt of hypochlorous acid with the chemical formula Ca(ClO)2.
Composition
After the gaseous and liquid products, the first solid chloro-product is treated here. Calcium hypochlorite Ca(ClO)2 according to DIN EN 900 is commercially available as an chlorine preparation in the form of tablets or granules. According to DIN it contains at least 65 % Chlorine. This high mass concentration of chlorine and the almost unlimited durability is an advantage of the product. Of course, the disadvantage is the sensitivity to water. Important are contained sub-components:
- 2 % calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 from the production and stabilization of chlorine.
- 10 % Sodium chloride NaCl affecting material compatibility, for example of stainless steel,
- 7 % insoluble parts of calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 and calcium carbonate CaCO3 as a cause for deposits and pH shifts,
- 5 – 10 % Hydrate water, these are water molecules incorporated in crystals.
Dosage as a solid
Calcium hypochlorite is, where the concentration of the disinfectant is unimportant, added as a solid in the water and dissolves therein. Examples are easy to find in some North African hotel facilities. If the concentration of the disinfectant is important, then the calcium needs to be resolved first and then dosed liquid. In water forms a suspension by precipitation.
For the disinfecting effect is not the added amount of calcium hypochlorite, but the content of the water free chlorine crucial. This refers to the substances, as dissolved elemental chlorine Cl2, as hypochlorous acid HClO and as a hypochlorite ion (ClO)– are present in the water. The mode of action is based on hydrolysis of the disinfectant to the hypochlorous acid.
Dosage in dissolved form
Contact between calcium arises with water an equilibrium:
That(ClO)2 + H2The ↔ 2 HClO + That(OH)2
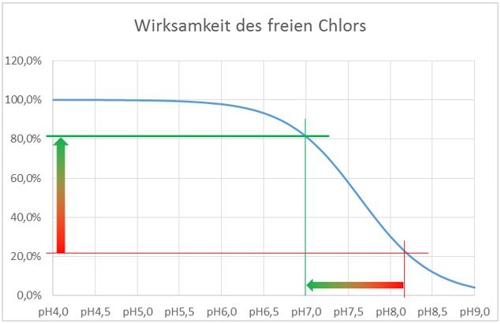
In acidic and neutral pH range, the hypochlorous acid is undissociated before. They dissociated at pH increases. Since the effectiveness of the hypochlorite anion is significantly less than that of the undissociated acid, the effect is highly dependent on the pH of the water to be disinfected. At pH values above 8,5 it is almost no longer exists.
After metering in water, the pH value of the water is raised by calcium. Lime present in the water thereby to precipitate and contaminate container or clog pipelines.
Application for drinking water storage
Frequently, if necessary, a calcium hypochlorite solution having a content of 14 g free chlorine produced in one liter of water, by a tablet is dissolved in one liter of clean heated water. As is to be expected with a high chlorine demand due to the high organic load by biofilms, starting from this solution depends on the volume of the water reservoir to a content of 0,6 mg / L free chlorine dosed.
risks
The risk associated with the use of solid calcium hypochlorite is mainly in the human actions. Mixing with hydrochloric acid HCl poses a particular risk. It would create chlorine gas in a very exothermic reaction.







Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.