Aerosols and dust as the source of infection with Legionella
Challenge of imagination
It has taken many years, until people have noticed, that water does not exist solely in liquid and solid form. The idea, that water dissolved in air is present in the environment, brings many people already to the edge of imagination. Many years ago Mr. Mollier has taken these states in a diagram and the dependencies of temperature and air pressure adds. To get an idea of the complexity of the issue, the diagram is shown under this section. In the diagram, a limit can be seen, in which the dissolved water passes in a form of small droplets. Below this limit is the "fog zone". The area is not to be confused with the morning traffic information. It features a state, in which our air is interspersed with so-called aerosols.
Aerosols
Aerosols, which you are breathing in are the mother of all Legionella problems. For this theoretical state there are many examples, in which people can be in a practical fog area. Usually these droplets separate from a larger, biologically seen healthy, volume of water. The droplets always also share a portion of the microorganisms living therein in the new habitat. From the perspective of micro-organisms, these droplets are huge and enter a universe for many species. Where to find infected aerosols, there is also found legionella.
The pictures show points, where people can come into contact with contaminated aerosols. Represented objects are by no means automatically contaminated with Legionella. These are examples only:
Who goes with open eyes through life, who finds very quickly other places, which can be potentially dangerous. Notes can be written in the comments.
Dust
In the section concerning the amoeba will be clear, that the Legionella can be well protected. This protection also ensures, that a drying out of the biofilm does not lead to killing of the Legionella. Will the dried biofilm be with the air, so as dust, spread, there is an equally high risk of infection.
Few of these species in biologically film are dangerous to humans. However, a risk arises from the increase under favorable conditions up to a number, which weakened humans can not fend off with the natural systems.
Legionella are everywhere. It just depends on, that the increase is not supported or even impeded.
 Loading...
Loading...
By Msimca [CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)], from Wikimedia Commons
The multiplication of legionella bacteria in the biofilm
In the video is within 2 minutes shown , how the biofilm within just 8 hours can spread.
Water from the source
Spring water is considered healthy and safe. Why? Because it is cold and comes out of the ground filter. There exists a balance between the bacteria. At the same time, the supply of nutrients for microorganisms is limited. Water from a well are attributed the same properties.
Cold, only few nutrients, in balance
But what happens to this water? It is transported in kilometer-long but poorly insulated pipelines, provided with the plastic of these pipelines or a phosphate dosage with nutrients and sometimes even brought by activated carbon or UV radiation out of balance.
Under certain circumstances, the water is stored separately in the sun, so that the shower works with pleasant warmth but without energy costs. What was an exception in the past, is now the rule. Here Legionella found in water temperatures between 25 ° C and 45 ° C ideal growing conditions. The optimum temperature for the legionella bacteria is 37 ° C. The inner surfaces of the water-supply systems are inhabited by a biofilm. This biofilm adheres as a slimy substance to the materials and provides an optimized habitat with protection and nutrition of the microorganisms.
Life in biofilm
The insulation of piping is connected with costs. Saving the isolation means heating the water and therefore an improved habitat for all organisms. The sum of these organisms nestles on the wall of pipes and tanks. This habitat is colloquially called a biofilm. The biofilm is also the basis for the multiplication of Legionella. It provides food and shelter. Because only the top layers of the biofilm can be achieved by disinfectants.
If the usual disinfectants have affected the upper layer, this does not mean, that the dead matter is rinsed. microorganisms recognize, if they can expand their habitat. Therefore incomplete disinfections cause a renewed and quite faster colonization of the gaps. While organisms with short reproduction times are at an advantage. Legionella doubled, depending on ambient conditions, all 2 to 6 hours.
Existing gaps through the disinfection will therefore accelerate the growth of the next generation. In addition, the living biofilm from adhering organic material can feed well.
For cyclical disinfection measures, there is therefore a disadvantage to be considered.
Water in nature

Source: www.pixabay.de
Illustration Biofilm
Source: www.fotolia.de
Biofilm in the microscope
Source: CDC/ Janice Haney Carr via Wikimedia
Life in the amoeba
Amoebas are small water animals, which feed oneself by other organisms. The amoeba or amorphous creatures are a big, diverse group of unicellular organisms, which have no fixed body shape, but change by forming pseudopods their shape constantly. Amoebas are a way of life, no kinship group. Amoebas are between 0,1 and 0,8 mm in size. Most species are naked; but there are also shelled forms.
Amoebas like to eat Legionella. Because their brain is extremely small, do not know the amoeba, that the Legionella are indigestible. The Legionella live and multiplicate in the amoeba. During this time the legionella are protected by the amoeba. The amoeba is not damaged too. If the legionella have shared several times, bursts the amoeba and sets the Legionella free.
Even killed by disinfectants amoeba is a protection and food for the next generations Legionella. Right a picture of an amoeba with different developmental stages of Legionella pneumophila.
A legionella is eating in the biofilm
Amoeba with Legionella
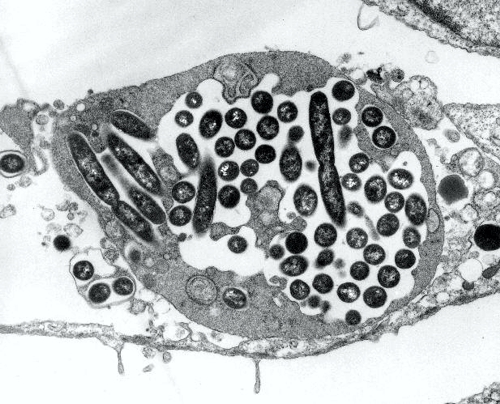
Source: by CDC/Dr. Edwin P. Ewing, Jr. [Public domain], via Wikimedia
Life in the activated carbon
The water treatment in filters must increasingly use activated carbon against colorings and flavors. The purpose is, to improve that water. On the surface of the activated carbon unwanted substances are deposited. It is important to know, that the surface of 4 equivalent grams of activated carbon corresponds to the surface of an entire football Square.
The attraction of the surface of activated carbon also affects the disinfectant. Therefore, activated carbon is also used to ozone in the water to reduce. The effect also acts on chlorine and bromine, because these disinfectants have a high binding force. So it is quite normal, that after passing through activated carbon, the disinfectants are already drawn out of the water after a short distance.
But the huge surface area of activated carbon is also a huge apartment for microorganisms. The biofilm thus can expand quickly without the effect of disinfectants. The carbon protects equally so amoebas and Legionella. Therefore, the activated carbon in water treatment is often a source of mulitplication of legionella. The disinfection with chlorine is almost impossible and associated with a huge effort.
Animation activated carbon with amoebae and legionella motile
For details on the instructions of the German Environmental Federal Office can be found at publications on the contamination of filters.
Legionella can multiply freely under the protection of the activated carbon.
The infection of humans
Water is not alone for drinking! Unfortunately, this old adage also has negative consequences. If you only drink the water, goes by the legionella little threat from. It is quite different, if the water reaches as an aerosol in the air and transported Legionella in this state. With the change in the shape of the aerosol a large pressure drop is often associated. This pressure drop can bring the Legionella pregnant amoebas burst. The additionally released Legionella increase the risk.
The microorganisms, which had a relatively normal life in the flying water droplets, found in the human lung ideal habitat. They multiply by leaps and bounds and the host is sometimes overwhelmed with the defense. The first (recognized) hosts were Legionaries of an army at a veterans meeting. The attacking species got the derived name "Legionella". So particularly old or debilitated people are prone to the disease.
The following film explained scientifically, how this infection of equip goes.
The statistics of the disease
Since the entry into force of the Infection Protection Act (IfSG) am 1. January 2001 there is a obligation to notify for the legionellosis. The data presented below for the year 2011 (Deadline 01.03.2012) based on the data, the Robert Koch Institute (RKI) forwarded in connection with the reporting obligation.
The following data are taken from Epidemiologisches Bulletin 50/2012 and 36/2018 the Robert Koch Instutes Berlin withdrawn. These are the results of the official reports.

Epidemiology
For the year 2011 were the RKI total 639 cases of Legionnaires' disease (Legionella pneumonia) transmitted according to reference definition. This corresponds to a nationwide incidence of 7,8 cases per million population. Compared to the previous year (692 cases of Legionnaires' disease, incidence 8,5 cases per million population) is the number of cases reported to 7,7 % declined. However, it had in January 2010 a large Legionella outbreak with a total 64 cases in the city of Ulm. This happened at the time to an increase in case numbers against 2009 (502 cases) to 37,8 % guided
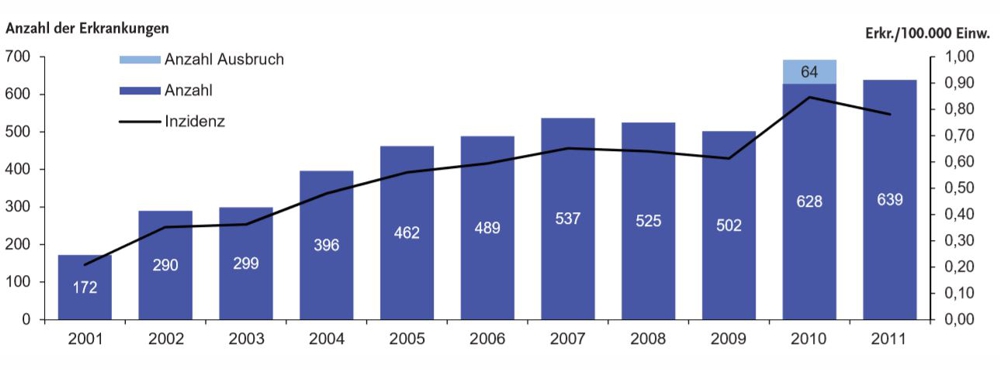
Source: Epidemiologisches Bulletin 50/2012 of Robert Koch Institute in Berlin
Mortality
At 30 diseased (22 men, 8 women) was 2011 the course of the disease so difficult, that they died of Legionella pneumonia. This corresponds to a mortality of 0,04 per 100.000 population. The lethality, ie the proportion of the deceased among the patients, scam 4,7 % and has thus over the previous year (51 registered deaths, lethality 7,4 %) decreased significantly. Illustration 4 shows the absolute number of registered deaths each year since 2001 and the percentage of dead among sufferers (lethality). The average age of the deceased was 2011 with 64,5 years (Median 69 years; span 0 to 85 years).

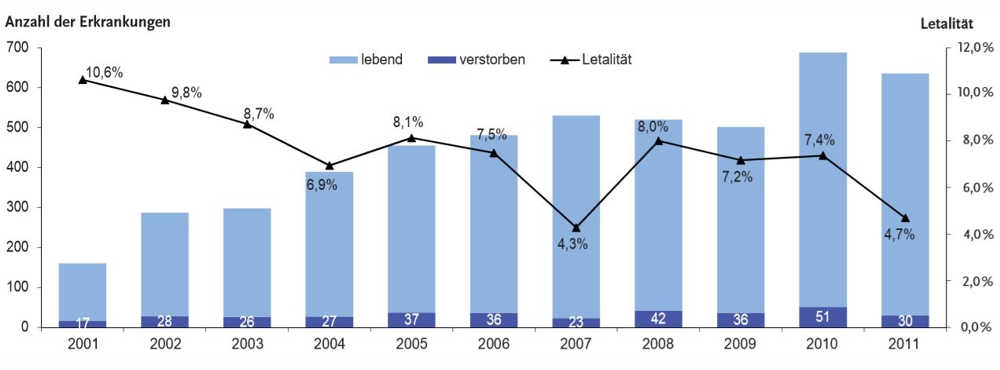
Source: Epidemiologisches Bulletin 50/2012 of Robert Koch Institute in Berlin
Update 2018
In another document, the Robert Koch Institute has the data, including 2017 evaluated. The number of cases has continued to rise significantly. The bright portions show the disease, that could have been related to a trip abroad.
One should not forget, that are counted in these statistics only diseases, whose link has been established for legionellosis. Because the disease of pneumonia is very similar, should the number of unreported cases in Germany to be very high.
Comparing to other nations have to draw even. But it can be assumed, that Germany represents the lower end of the number of diseases and death rate due to the extremely high standard in the sector of water treatment.
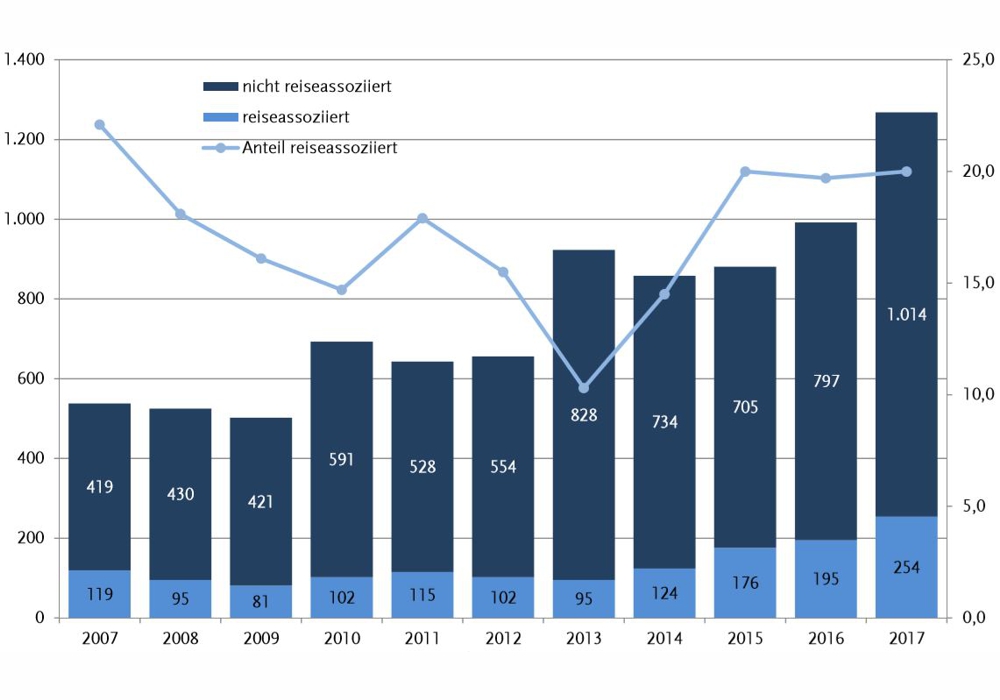
Source: Epidemiologisches Bulletin 36/2018 of Robert Koch Institute in Berlin
The players in the Legionella-fight
Pay attention, in particular the following texts, but generally all texts in this website, do not represent, as described in the imprint, no legal advice or represent score. It is exclusively the opinion of the author. The following depiction illustrates the environment in Germany.
One should distinguish first, which group one belongs. General following groups are involved.
The order of the following groups is ordered according to the perceived risk of harm. Therefore, the list begins with those affected. By chance, the reverse sequence corresponds to the apparent influence of these groups. It may be beneficial, to read this section starting with the insurance DGUV in reverse order.

The affected
The affected people are or were the direct risk of infection exposed to Legionella. From damage arise rights, if the polluter or a violation of the law can be detected.
If the affected does not belong to another group, then the advice applies, to go through life with open eyes and to be suspicious when aerosols. Especially if the person is weakened or ill, he should avoid aerosols in its environment. Here, the examples are shown again:
The owners
The owner of a water supply system or (and only a few people are aware of) a building, where people can be exposed at risks of harm, are here addressed. This includes owners of apartments, which are leased.
Also owns a refrigeration plant with an open cooling tower or cooling with spray mist in the restaurant or a spray plant in the greenhouse or other facility, which spread by aerosols in the area, are in this group. The necessary examples are shown above.
A plant owner can of course simultaneously operate the plant. An owner can of course simultaneously operate the plant. He even explained virtually for a professional entrepreneurs. He even explained virtually for a professional entrepreneurs.
For this group, the obligations apply, arising from property. Whether it is the owner is a natural or a legal person, is not important.

Also missing technical knowledge on the subject of Legionella do not protect against the risk.
It is a common mistake too, that the risk and the liability can be contractually passed on to a specialized company. For the owner, it is important, to follow the instructions of the specialist companies and to know their duties.
Here's an example, in which a text of an authority is assigned the duty . In the example of drinking water, Quote Federal Ministry of Health: The current drinking water regulations contain regulations regarding Legionella investigations in drinking water heating systems of the drinking water installation. Affected by the obligation to examine Legionella are entrepreneurs or others owner of a drinking water installation,
- in which the drinking water at a public (for example. in playschools) or commercial
(for example, rent out apartments) activity is delivered and - which contains a large plant for heating drinking water and
- contain showers or other facilities, where there is a misting the drinking water comes (So not the hand basin in the toilet of the restaurant).
Under the obligation to inspect fall schools and playschools as well as houses with rented out apartments or hotels, if there is a large plant is operated with hot drinking water. As large plants apply
- Water heaters with more than 400 liters content or
- water installations with one or more pipes with a volume of at least 3 liters.
Owner communities in rise condominiums of the examination shall only be required to comply, if at least one apartment is rented out in the building.
The complete document of the Federal Ministry of Health can here are displayed.
The specialist companies
Frequently the operation of a water supply is- or water treatment system is passed to a so-called operator. Of course, these operators must possess the necessary knowledge in this field.
Wikipedia: As a specialist company is described an organization with professional competence in a particular sector.
The entrepreneur is therefore a high level of expertise in his field, here on the field of the water treatment or water supply, assumed. The degree of this expertise goes beyond the so-called "general rules of technology". The skill of the entrepreneur of publications in the special press had assumed and should be expected, this was the opinion of the Higher Regional Court of Frankfurt. For that reason can be assumed, that the owner or the operator has sufficient knowledge about Legionella and related rules.
For the specialist entrepreneur, the liability risk is of crucial importance. The specialist entrepreneur is thus to guess, to know the rules and regulations in force and to comply. It is necessary, to attend regular training of the associations and to fix this knowledge in all levels of the company.
Violations of the rules (or the human mind), which the specialist entrepreneur can recognize, he must notify his client. At one obviously wrong planned facility it may even be necessary, stop work independently. It does not matter, whether the breach was caused in their area of responsibility or a third party responsibility.

The specialist entrepreneur has the control measures taken by the authorities and organizations know and enable. Moreover, the specialist entrepreneur needs to know measures and actively offer, which limiting or prevent the spread of Legionella. These measures may be selected of the field of prevention, the disinfection or the probiotic displacement. The specialist entrepreneur has to be able, to advise the customer so both technically and economically . He compares the effectiveness and costs of different methods “contra legionella”.
The certified sampler
The quality, pollution control and verification of the drinking water is regulated by the drinking water regulations. The review of the drinking water is one of the responsible and therefore precisely defined tasks. In other rules is determine, when and where samples must be taken. To meet the physical, chemical and biological requirements for a correct sample, may laboratories use only "certified sampler" . Errors in the sampling can not be by even the best laboratory services “heal”. The requirements apply not only in the field of drinking water but also for process water in industry or wastewater. This representation of the connection is therefore only an example.
The drinking water regulation provides for the officially recognized investigations (according to. §14 TrinkWV) out, that investigations be carried out by such laboratories, which the accreditation by a recognized office (in Germany DAkkS) can prove (according to. §15 Abs. 4 TrinkWV). This regulation also includes the sampler, who must have completed appropriate training and thats wy will become “adequately qualified personnel". In addition, the accreditation standard DIN EN ISO demand 17025 the impartiality of the sampler. Thus, there must be no relationship of dependency between sampler and clients of sampling. The sample, which is intended for an official assessment, so DO NOT performed by its own personnel of the owner of the plant.
Note: So if the sample is NOT intended for regulatory judgement, it's allowed to take the test and also examine its by own staff.
Quote State Environmental Agency NRW (Nordrhein-Westfalen): The execution of a representative, task-oriented and legally unobjectionable sampling is the first part of each step analytical investigation. , it has a special significance, because errors in sampling usually can not be corrected even by the most complex analytical and statistical measures. On the other hand, these mistakes can often be recognized with little effort and eliminate. In addition, the equipment costs for obtaining a representative sample are very low compared to the costs in the laboratory sector. The full document here.
Source: Environmental Agency NRW, www.lanuv.nrw.de/fileadmin/lanuvpubl/0_lua/
The sampler may inadvertently or intentionally influence the result of the sample. Here are a few examples of the factors, which may affect the outcome:
- Sampling time, for example, before or after a rinse of the system,
- Place of sampling, for example, in a "dead" area,
- Sterility of the container, already with the breath germs can be entered
- Flaming of the sample site, to short heating can lead to the spreading of germs of the outlet,
- Sufficient lead, to short lead yields no result to the main pipeline,
- Neutralization of disinfectants. The possibly existing remnants of disinfectants must be immediately neutralized so that the result is not falsified. For this, the disinfectants used and their neutralization partners must be known and available.
- Cooling the sample. Legionella have a very short reproduction rate. Therefore, the increase must be performed by an instant cooling at the transport temperature during transportation to the laboratory. Especially hot water from a cooling tower is often actively cooled immediately. An insulating packaging reinforces this error!
- Transportation time and transportation conditions to the laboratory
The drinking water regulation provides for the officially recognized investigations (according to Section 14 Drinking Water Regulations) out, that investigations be carried out by such laboratories, which the accreditation by a recognized office (in Germany DAkkS) can prove (according to §15 Abs. 4 drinking water regulation). This regulation also includes the sampler, who must have completed appropriate training and thats wy will become “adequately qualified personnel". In addition, the accreditation standard DIN EN ISO 17025 the impartiality of the sampler. Thus, there must be no relationship of dependency between sampler and clients of sampling. The sample, which is intended for an official assessment, so DO NOT performed by its own personnel of the owner of the plant.
Note:
So if the sample is NOT intended for regulatory judgement, it's allowed to take the test and also examine its by own staff. An investigation with results within an hour with the Mobile Legionella Laboratory possible.
The accredited laboratory
In the interest of quality of work and in the interest of uniform standards, by public authorities only results will recognized , which by a "accredited" laboratory were developed. For this, the laboratory will by the German Accreditation Body (DAkkS) for compliance with quality standards according to DIN EN ISO / IEC 17025:2005 checked.
In addition, the laboratory must use methods for investigation, for which a accreditation exist, or the laboratory must certify and accredit leave their own methods.
Requirements for an accredited laboratory, for example by the Bavarian State Office, are very well defined. Quote: Investigation labs (Testing labs), which microbiological, physical, physicochemical, chemical, who want to carry out sensory examinations including sampling under the Drinking Water Regulations … and not are approved for drinking investigation laboratory in any other State, must submit an petition … the Bavarian State Office for Health and Food–Safety security. The full document here.

Through this extensive control of accreditation results of laboratories are very reliable.
There is still a significant impact on the counter-measures. By the method of investigation elapse between sampling and results about. 12 days. The damages, that may have occurred in the meantime by "ignorance", are probably difficult to insure.
In addition to the tests required by a laboratory the concentration of legionella itself can be checked. A device for these studies described here.
The German Association for Gas- and Water e. V. (DVGW)
From the numbers and spread of the memberships shows, that can also be a weighting occur in representing different interests. The association is organized into committees and worked among others for device data sheets and test rules. Failure to comply with these leaflets and rules will increase the risk to producers and sellers of technical equipment. Usually the rules are used by German courts as a benchmark for the technical level but also for the security measures.
About a direct testing of systems or equipment for compliance with the rules of the DVGW can be a (paid) Certification of accordance be achieved . This can mean a competitive advantage for companies in Germany. However, the so-called machinery directive of the European Union is based on the standards level of DIN EN ISO, so that compliance and the required declaration of conformity are formally sufficient for placing it on the market. The own explanation, to conform to the rules of the DVGW, however harmless and are adequate for most situations. Some examples of existing rules:
- W 229: Process for the disinfection of drinking water with chlorine and hypochlorites
- W 224: Process for the disinfection of drinking water with chlorine dioxide
- W 294-1: UV devices for disinfection in water supply; Part 1: Demands on quality, function and operation
- W 294-2: UV devices for disinfection in water supply; Part 2: Testing of constitution, function and disinfection effectiveness

- W 557: Cleaning and disinfection of drinking water installations
- W 624 (A) December 2015, Metering systems for disinfectants and oxidants; Preparation- and dosing of chlorine dioxide,
A complete list can't be viewed here: https://www.dvgw-regelwerk.de/plus/
The contents are copyrighted and can therefore here (not even in part) being represented.
For the current topic, the individual publications are very helpful to get an idea of the possibilities on the national market. The disadvantage, that new technologies do not reflect in the rules and only have to go the hard way of market penetration.
At the same time the rules is of course a great instrument of power of the dominant German companies, which sometimes new developments- prevented.
Wikipedia: The German Association for Gas- and Water e. V. … is the trade association of the German gas- and Water Management, based in Bonn. The association is concerned in self-government with technical and scientific tasks of the fuel gas- and water supply.
Its main task is the creation of the Technical Regulations, improve the safety and reliability of gas- and water supply is ensured.
The experts of interested parties create in voluntary cooperation, the DVGW. That means, Although the technical rules for gas- and water industry can be developed by the industry itself (Technical self-government).
Here can Recognized rules of technology (Aart) arise, is the frequently made in legislation regarding. Compliance with these rules is no compulsion. However, they are standard in the case of damage, and they can in terms of liability law virtually come "legislative acts", provided that the underlying law so provides. For example, must then be detected in case of damage, that at least the recognized rules of technology have been complied with.
The DVGW was 1859 was founded in Frankfurt am Main and 2013 exactly 13.541 Members, among them 1.903 Utilities, 1.386 companies, 252 authorities, institutions, organizations and 10.000 personal members.
The Association of German Engineers e. V. (VDI)
The economy close of the VDI takes a positive in the rapid practical support through technical rules for new problem areas. Thus, shortly after the first Legionella cases, the decision of the leaflet was made
VDI 2047 sheet 2: Ensuring the hygienic operation of evaporative cooling systems
The contents are copyrighted and can therefore here (not even in part) being represented. This leaflet gives an insight, which measures help in a Legionella infection and required by the VDI. Relevant content is discussed elsewhere.
By the state, the standard VDI was 2047 sheet 2 in the Regulation "42. BImschV" adopted and thus become law.

These "The Forty-Second Regulation implementing the Federal Immission Control Act (Regulation about evaporative cooling equipment, Cooling towers and wet scrubbers – 42. BImSchV) from 12. July 2017“ is also discussed in the section "Cooling towers".
Wikipedia: The Association of German Engineers is a German technical and scientific association. The VDI Group consists of in a non-profit organization (short: VDI e.V.) and the VDI GmbH with its commercial businesses.
The VDI e.V. is according to own data the largest union of engineers and natural scientists in Germany. He sees himself as a lobbyist for organized in him engineers and scientists, but describes itself as opposed to other stakeholders in technical professions officially called "economic-close".
The European Union
The EU has set itself the goal, to reduce the number of products available on the market biocides. In the underlying policy but was overlooked, that a high proportion of the biocides are produced locally. For this purpose a Biocidal Regulation enact.
The best known and probably the same time most critical example of the gap is the electrolytic production of chlorine from salt. Since the composition of the salts, composition of the water and power density of the electrodes can vary, the product can considered as a mixture of many biocidal substances. Although the process has been playing a role for many decades, at least in Germany a violent discussion with the authorities has developed. The European Commission has at least recognized this gap and in a meeting (Document link on the Protocol to the 59. meeting) busy with.
Electrolysis of chlorine
The consideration of the gap for the electrolytic process seems understandable. Is the process yet dynamic and depends on the time and place of an examination of the composition. Unlike the situation should be assessed for chlorine dioxide. In the biocide regulation distinguishes between a list of "known existing substances" and new biocides.
Chlorine dioxide to the chlorite-acid method
Both the precursors (starting materials) and the product of the chlorite acid process are listed in the list of known substances (and thus can also be traded before an exam). The review of the chlorine dioxide is associated with the individual state Portugal to the list.
In the year 2014 the Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health published its views on the legal situation in the presentation “Scope of the new Biocides Regulation“.
The opinion of the Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health for the implementation of the Biocides Directive (Document link to the Biocidal Regulation) is also in an information “The new biocide regulation” reproduced. No guarantee can be given for the accuracy of the source.
Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Document: „Am 1. September 2013 releases the new biocide regulation (EU) No. 528/2012 the former Directive 98/8/EC as from. The new regulation includes, among other changes in the authorization of biocidal products. For products with a low environmental- and health profile a simplified method is provided. In addition, now treated with biocides goods is recognized. In addition to new labeling requirements may contain only active substances, which are marketable in the European Union. Under the new regulation, the use of in situ produced desinfectants is regulated (as exampla ozone). In consequence of the change of the legal basis there will be new requirements for application documents. There are also innovations in the formal requirements for the authorization of biocidal products, for example in the submitted formats and deadlines. "
Biocidal Regulation
Biocidal Regulation (EU) No. 528/2012, (3): "The purpose of this Regulation is, to improve the free movement of biocidal products within the Union while ensuring a high level of protection of human and animal health and the environment. …“.
Biocidal Regulation (EU) No. 528/2012, (3): ... In order to eliminate "barriers to trade in biocidal products as much as possible, should rules on approval of active substances and the making available on the market and use of biocidal products, including rules on the mutual recognition of authorizations and on parallel trade, be established. "
Biocidal Regulation (EU) No. 528/2012, (26): "In order to provide certain biocidal, have similar using conditions in all member states , to facilitate the market throughout the Union, it is appropriate, provide an EU-wide approval for these products. …“Already especially not is an indication in the biocide regulation of "one country-specific approval for the by this (a special) plant (from one manufacturer) generated (Biocidal product) Chlorine dioxide" is mentioned.
Biocidal Regulation (EU) No. 528/2012, ANNEX VI, COMMON PRINCIPLES FOR THE EVALUATION OF DOSSIERS FOR BIOCIDAL, rating, Introduction, point 6: "In the case of in situ generated active substances also with the precursor(s) included possible risks from the risk assessment. "and
point 14: "Insitu agents and made the appropriate precursors are also included."[6].
The process for the production of chlorine dioxide from the aforementioned precursors is the hydrochloric acid-chlorite method and is described in the literature as well as in the worksheets of DVGW. Thus, not "plants for the production of chlorine dioxide on site" but three substances are tested, namely by an authority from the "rapporteur Member State". So it could be, that the manufacturer of the on-site generation plant is assigned the role of the producer, the "Products provides".
Biocidal Regulation (EU) No. 528/2012, (2): "Biocidal products should be made available on the market or used must, if they have been approved in accordance with this Regulation. …“
Biocidal Regulation (EU) No. 528/2012, (7): "It should be between existing active substances, which were on the date stated in the Directive 98/8/EC implementation date in biocidal products on the market, and new disinfectants, were not yet to that date in biocidal products on the market, be distinguished. During the ongoing review of existing active substances, Member States should continue to allow, that biocidal, containing those substances, may be provided according to their national rules on the market, until a decision is taken on the approval of the active substances concerned. …“
The List of "known existing active substances“ found in REGULATION (EG) No. 1451/2007. Here are both the precursor sodium chlorite (EG-Nummer: 231-836-6, CAS-Nummer7758-19-2) and the active chlorine dioxide (EG-Nummer: 233-162-8, CAS-Nummer: 10049-04-4) listed as identified existing active substances.

The active ingredient chlorine dioxide and its precursors identified as existing active substance, and therefore subject to a revision of the "national rules“, the further deployment of the active substance "should allow further“.
A national requirement, which of this principle (that the continued provision of the substance should not be permitted), is the author currently not known. Rather, you can see the drinking water regulations as "national regulation" to understand the use of chlorine dioxide. Accordingly, by the drinking water regulation the use of the active ingredient chlorine dioxide as a preparation material for the disinfection of drinking water as "national regulation" expelled.
This relationship could be regarded as official permission, allow chlorine dioxide to be produced on site by means of an on-site production facility until completion of the ongoing inspection.
The List of "known existing active substances“ found in REGULATION (EG) No. 1451/2007. Here are both the precursor sodium chlorite (EG-Nummer: 231-836-6, CAS-Nummer7758-19-2) and the active chlorine dioxide (EG-Nummer: 233-162-8, CAS-Nummer: 10049-04-4) listed as identified existing active substances.
The active ingredient chlorine dioxide and its precursors identified as existing active substance, and therefore subject to a revision of the "national rules“, the further deployment of the active substance "should allow further“.
A national requirement, which of this principle (that the continued provision of the substance should not be permitted), is currently not known. Rather, you can see the drinking water regulations as "national regulation" to understand the use of chlorine dioxide. Accordingly, by the drinking water regulation the use of the active ingredient chlorine dioxide as a preparation material for the disinfection of drinking water as "national regulation" expelled.
This relationship could be regarded as official permission, allow chlorine dioxide to be produced on site by means of an on-site production facility until completion of the ongoing inspection.
Follow the classification of biocides by regulation in product types.
Product Type 2:
Disinfectants and algaecides, which are not intended for direct application to humans or animals Products used for disinfection of surfaces, textiles, equipment and furniture, which not for a direct touch with life- or feedstuffs are used. The application areas include, inter alia, swimming pools, aquariums, bathing and other water, air conditioners and walls and floors in both the private and the public and industrial areas and in other areas used for professional activities. Products used for disinfection of air, not for human or animal use water used, chemical toilets, sewage, Hospital waste and soil. As algaecides for swimming pools, aquariums and other waters and for remedial treatment of construction materials used products. Products as an additive in textiles, tissues, masks, Paints and other articles or substances, to produce treated goods with disinfecting properties.
Product Type 3:
Veterinary hygiene, Products for veterinary hygiene purposes such as disinfectants, disinfecting soaps, Products for body- and oral hygiene or with anti-microbial function. Products used for disinfection of materials and surfaces associated with the housing or transportation of animals.
Product Type 4:
life- and animal feed products for disinfection of equipment, containers, Cutlery and crockery, Surfaces and lines, in connection with the preparation, transport, storage or consumption of food- or feed (including drinking water) are used for humans and animals. Products used to impregnate materials, which may come into contact with food.
Product Type 5:
drinking water products used for disinfection of drinking water for humans and animals.
Product Type 11:
Preservatives for liquids in cooling- and processing systems products used for preservation of water and other liquids in cooling- and processing systems by the control of harmful organisms such as microbes, algae and mussels. These product type exclude products for the disinfection of drinking water or of water for swimming pools.
Product Type 12:
Slimicides products for the prevention or control of slime growth on materials, equipment and structures, find in industrial processes, for example, on wood and paper pulp, porous sand layers in oil production.
Product Type 20:
Control of other vertebrates products used to control other than vertebrates, which are currently covered by the other product types of this main group, by means other than repulsion or attraction. (for that product the non-inclusion is decided)
The discussion about Insitu products is not finished by far. In the Protocol to "59th meeting of representatives of Members States Competent Authorities for the implementation of Regulation 528/2012 concerning the making available on the market and use of biocidal products" the need for further discussions will significantly.
German Lawful Accident Insurance e.V. (DGUV)
Dealing with disinfection means and disinfection systems is always associated with a risk. This risk is assessed in the DGUV and formulated to rules. The safety regulations, for example for the use of chlorine dioxide plants the UVV d5 chlorination of water, are summarized by this umbrella association or when required for use. Since besides chlorine and chlorine dioxide, and its in-situ production detected in this insurance provision, reading can be recommended.
Rating
Legionella are recognized as a risk to humans. Therefore, the insurance probably has in each measure the proverbial “last word”. Because a plant, that can not be insured, can not be used ultimately. If in doubt, the insurance should always be sought should!
The German Lawful Accident Insurance
The Lawful accident insurance is the top federation of accident insurance. The history of the lawful accident insurance begins in the second half of 19. century. Rapid industrialization changed the formerly rural country. Factories shooting literally from the ground.

On one hand, they provide new jobs and are also urgently needed due to population growth.
There are also other new tasks: With the 1996 concluded the Seventh Social Code (SGB VII) and the Occupational Safety and Health Act of prevention behalf of the accident insurance is extended again. It now includes in addition to the prevention of occupational accidents and occupational diseases and the defensive work-related health hazards – such as back pain or mental stress. To be in this new field of work, Accident Insurance is seeking greater cooperation with the health insurance. In addition, the SGB VII confirms the established principles of statutory accident insurance.
Cooling tower, Drinking water, Aquapark, Fountain
The agencies and public authorities
… take up the rules and leaflets of the aforementioned associations and make laws out of it, that fit the topic. Since different authorities and different rule-writers to work the rules arising are not always compatible with each other. It is then to be tried, to put the relationship in a logical reference. The reasoning lines of the current ranges are therefore here divided into:
- Cooling towers,
- Drinking water systems,
- Filter systems for pools,
- Fountains in public spaces (in preparation),

In the field of cooling towers
From the statistics on Legionella at the Robert Koch Institute seems likely, that the emission of Legionella via the aerosols of open cooling towers has caused the largest proportion of sick and deceased people. The VDI has with his rule 2047 sheet 2 responded. Fittingly, the state has around the rules of the VDI 2047 sheet 2 a regulation "42. BlmSchV" arranged, which should ensure the monitoring of compliance with the VDI rules. There are exceptions defined and fixed duties, but not the VDI 2047 sheet 2 textually cited.
In the introduction of VDI 2047 sheet 2 "Ensure the hygienic operation of evaporative cooling systems" is justified: "Projections showed, that in Germany with about 15 000 to 30 000 outpatient acquired legionella pneumonia per year must be expected, which may be caused in part by evaporative cooling equipment. Examples are the legionellosis outbreaks in Ulm in 2010 and in Warstein in 2013. "
Knowledge of the VDI
The directive VDI shows the need for action in the following text. VDI 2047 sheet 2 Paragraph 9.3.2.1 Regular laboratory tests: Legionella spp.
Legionella spp. are pathogens, whose transmission takes place through respirable aerosols (…). The presence of Legionella in the circulating water is not detectable by the parameter "general colony number" nor by other indicator bacteria. Thus, a direct detection of this human-pathogenic bacterium as defined in health is essential.
The content of the Directive then provides but a major limitation to the beginning: VDI 2047 sheet 2 Paragraph 5.3 Use of biocides: On the use of biocides is, whenever possible, to renounce. The use of biocides is governed by the regulation (EU) No. 528/2012 (Biocide - BPR) and the GefStoffV - Hazardous Substances Regulation. It may by BPR only approved biocidal products of the corresponding product type (PT 11 for cooling water) be used. The German approval body for biocides is the Federal Bureau of chemicals of the Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (BAuA).
Precipitation in the biocidal regulation
The cited biocidal regulation has "forgotten" the in-situ products and put probably in a big discussion, please refer protocol to 59. Meeting of the authorities of the EU Member States, to the regulation still be regulated. Details and complete content Biocidal Regulation are readable in the section "The European Union". Subsequently, further quotes from the VDI 2047 received:
The first impression of the risks from the operation of cooling towers is confirmed. VDI 2047 sheet 2 Paragraph 6 Health risks: In evaporative cooling systems, biofilms develop mainly due to the water-wetted surfaces
piping,
- heat exchangers,
- filling bodies and
- drop seperators.
The growth of the biofilm is enhanced by
- mineral deposits,
- dirt,
- sludge and
- corrosion products.
The mass of the biofilm depends on various factors. Examples are:
- quality of the water and the ambient air
- Temperature and nutrient concentration in the water
- hydraulic conditions
- used materials
- light
- presence of biocides
From biofilm microorganisms are continuously released into the circulation water. Of particular relevance from a health perspective here is the release of pathogens (for example, Legionella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa). (…) There are indications of increased virulence of Legionella, which have multiplied in amoeba. (…) Legionella, which are protected against dehydration in amoebic cysts, however can be spread as airborne particles over long distances. (…) In very cold weather with temperatures below freezing may occur lyophilization. Legionella can survive longer in this case. The entry of individual Legionella in water-bearing systems can not be prevented. In order to reduce the risk of infection, it is therefore of particular importance to minimize the spread of Legionella and to reduce the release of aerosols. Also when performing cleaning- and maintenance work may lead to inhalation of high concentrations of Legionella.
The fight against legionella becomes the regulation
A justification, to actively fight the legionella, provides VDI 2047 sheet 2 Paragraph 8.7.1 Water treatment and water care: The multiplication of microorganisms, which can form biofilms, must be reduced, because biofilms can be a habitat for pathogens such as Legionella. Biofilms also lead to disruptions of the heat transfer, to deposits in control valves and probes and promote corrosion.
It does not help, only install a disinfection, it is alsoto check the interaction with other additives and materials . VDI 2047 sheet 2 Paragraph 8.7.1.2 Treatment of the circulating water: (…) Important note: Additives can promote the multiplication of microorganisms. This particularly applies to biologically usable substances, for example, inorganic phosphates. (…)
Nevertheless, measures and means to combat microbiological load are displayed in the same section:
Limiting microbiological contaminants
- biocides
- UV radiation
For the use of biocides see also section 5.3. Examples are:
Oxidizing biocides
- inorganic chlorine- and bromine compounds
- organochlorine- and bromine compounds (Halogen splitters such as Bromchlordimethyl-hydantoin (BCDMH), Monochloramin, Chlorphenol, Di-Chlorisocyanurat)
- Chlorine dioxide
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Peracetic acid
- Ozone
Non-oxidizing biocides
- quaternary ammonium salts
- Glutardialdehyd
- organic sulfur compounds (Isothiazolinone, Tetrakis (hydroximethyl) Phosphoniumsulfat (THPS))
- organobromine
- organochlorines
Physical treatments
- UV radiation
Interesting is, that biological processes do not play a role despite the better environmental balance. The Probiotic displacement is described in another tutorial. But in VDI 2047 sheet 2 is addressed on particularly critical points, which may limit the choice of the biocide. VDI 2047 sheet 2 Paragraph 8.7.1.2.1 Use of biocides: In particular play (…) pH, the temperature in the circulation water (…) an important role.

Measurement- and control technic
The demands on measurement- and control technology will be significantly expanded. Was it earlier still common, to allow the replacement parameters "redox potential" as proof, is this notice very clearly: VDI 2047 sheet 2 Paragraph 8.6 Recommendations for measurement and control technology: A high degree of operational reliability of an evaporative cooling system can be achieved by remote monitoring or data acquisition and centralized evaluation (…) be achieved. It is recommended to monitor important operating parameters:
(…)
Conductivity of the circulating water
Disinfection
- Biocide dosing (Metering pumps and level of dosing storage tanks)
- Concentration of the biocide in the circulating water
(…) As a control variable for dosing amperometric or direct-photometric measurement methods can be used. The measurement of the redox potential is only suitable as a monitoring parameter.
In this short formulation, the need is hidden, to be able to measure the concentration of a biocide. In order to implement this, the biocide must be known in its composition. This usually does not apply to "blends from the chemical company kitchen", on products based on chlorine dioxide, Chlorine- or bromine yes. Possible limitations can also be Biocide regulation of the European Union from 2012 to be read. In the version 1451/2007 is the “List of identified known substances " from about. Page 10 printed.
For remote monitoring of the operating parameters the controller can DOSAControl DCW 400ip and the sensors of series DOSASens be used. If you forget the remote data transfer and storage, then it comes down to the built-in timer, to meet the following text. An example of the specialization on the timer also form devices Ecolab or Walchem.
Design requirements
But the dosage of a disinfectant alone, albeit under favorable conditions, is not a panacea. Regularly also errors in the design of the plant must be corrected. The regulation states in this: VDI 2047 sheet 2 Paragraph 8.7.1.2.1 Use of biocides: Important note 2 Biocides may not penetrate into stagnant or low flow areas or may be insufficiently concentrated. That means, that these areas of the water cycle to ensure the necessary reduction of microorganisms by constructional measures, such as cutting off dead pipes, or by operational measures, like a flushing regime, must be minimized. A locking of the desalination during the duration of the dosing and a definable follow-up time, taking into account the water regulations (For example, waste water regulation, attachment 31) is to be provided.
VDI 2047 sheet 2 Paragraph 8.8.3 Initial filling and testing of water, water quality: Before receiving the test- or intended operation, the evaporative cooling system is filled with water. The chemical and microbiological quality of water at the transfer point and their variability is necessary before filling. It should be checked at least the following parameters:
- Colony forming units
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Legionella spp.
The filling may only take place, if the water quality does not expected any negative effects on the hygienic operation of the system. The results of these analyzes and the filling of the plant should not exceed seven days.
Important note: The provisions of section 8.5 must also be observed in trial operation.
Also, whereas it is a necessity, to be able to carry out the measurement of legionella very quickly.
Before sampling the water is at least 30 s to run.
comment: This is contrary to the directive for the sampler.
Intervals of the investigation
Important note 1: The sampling must be done so, that it is not distorted by biocide dosing. The sampling point must be upstream of the biocide dosing.
Due to changing environmental conditions (for example, temperature, quality of the raw water, input of nutrients) resulting in fluctuations of the microbiological quality of the circulating water. A close examination interval, for example, monthly, therefore makes sense. The Legionella tests are at least quarterly perform.
comment: Since the year 2000 The current requirements of the British Bureau of Occupational Health and Safety include a WEEKLY monitoring of the concentration of Legionella in circulating water.
Legionella spp.
Legionella spp. are pathogens, their transmission takes place by respirable aerosols (see section 6). The presence of Legionella in the circulating water is not detectable by the parameter "general colony number" nor by other indicator bacteria. Thus, a direct detection of this human pathogenic bacterium in terms of health protection is indispensable.
Investigation Methods
Already at this point it must be noted, that the examinations are standardized for Legionella although, but these standards have a considerable variation itself. It would certainly be helpful, to make the statistical fluctuation range of Legionella tests known in assessing the condition of a cooling tower.
Outside the standardized but very inaccurate and slow examination methods, there is the possibility, own results with the Mobile Legionella Laboratory to obtain
VDI 2047 sheet 2, Table 4. Measures, depending on the concentration of legionella
Legionella spp. in KBE/100ml
<100
Activities
- none
Legionella spp. in KBE/100ml
100 to <1000
Activities
- reexamination, on confirmation of the concentration microbiological tests in a monthly rhythm
Legionella spp. in KBE/100ml
1000 to <10000
Activities
- immediate shock dosage biocide
- Causes- Determination, including an inspection (see table 1 and section 9.3.1) and removal of defects, optionally adjusting the operation of
- renewed microbiological tests on a monthly rhythm; on confirmation of the concentration control of water treatment and water care (if necessary, disinfection) and correction
- optionally increasing the number of sampling points (see section 9.3)
Legionella spp. in KBE/100ml
10000
Activities
Immediate danger prevention is necessary.
- It must be remedied immediately according to the catalog of measures for incident management,depending on the system, for example,:
- shock dosing biocide increasing the blowdown drain
- cleaning and disinfection
- Implementation of structural and operational measures
- Verification of efficacy by timely additional microbiological examinations in the absence of rehabilitation success
- Decommissioning of the plant
- Starting of further remedial measures
- on re-commissioning immediate microbiological examinations (see initial start-up section 9 3)
- Measures to protect employees and third parties
In the field of drinking water systems
A major topic is of course the drinking water supply. Here end the rules of DIN, DVGW and VDI regularly in the known drinking water regulation.
The justification of the measures is in paragraph 5 5 witch drinking water regulation anchored. In the (for the purpose of legibility) shortened form states:
So far (…) an agent (…) facts discovered, which to occurrence of a transmissible disease (…) being able to lead, (…) must a preparation, if necessary, including a disinfecting (…) be done. In piping networks (…) where the requirements (…) can be met only by disinfection, have the (…) owner (…) a sufficient disinfection capacity by free chlorine, Chlorine dioxide or other suitable disinfectants or procedures (…) keep ready.
The following quotes apply to Legionella:
f) Legionella: The tests on Legionella spec. is in accordance with ISO 11731 and DIN EN ISO 11731 Part 2 carry out taking into account, if appropriate, present recommendations of the Federal Environmental Agency.
In Part II is for the indicator parameters Legionella spec. a Technical measures value 100 CFU per 100ml set.
b) Analysis of drinking water installations according to § 14 Paragraph 3
Der Parameter Legioonella spec. is at least once a year in accordance with the provisions in § 14 paragraph 3 to investigate. Wasserversorgungsanlagen nach §3 Nummer 2 Letter e, from which part of a commercial, but not public activity is delivered drinking water, are at least every three years relevant provisions of § 14 Paragraph 3 to investigate. The first examination must reach the 31. December 2013 to be finished. For water supply systems according to §3 number 2 Letter d The Health Authority specifies the frequency determined.
Are on the annual tests for Legionella spec. has found no cause for three consecutive years, so the health department can also set longer examination intervals of up to three years, provided that the system and operating mode have not been changed and demonstrably comply with the generally accepted rules of technology. This temporal extension of the examination intervals is not possible in areas, in which patients are at higher risk for hospital infections (as hospitals, Care facilities and rehabilitation centers, Facilities for outpatient surgery, Dialysis facilities, childbirth facilities).
Number and description of representative sampling points according to § 14 paragraph 3 Sentence 1 governed by the generally accepted rules of technology. Sampling is carried out in accordance with DIN EN ISO 19458 as there under ,,purpose b” described. The amount of water drained before filling the sample container is allowed 3 liters not exceed. (compare cooling towers VDI, "not more than 30 seconds ")
Requirements of drinking water regulations 2016
§ 5 Microbiological requirements
(5) As far as the entrepreneur and the other proprietor of a water supply- or water recovery plant or a representative of them in terms of microbial loads of the raw water facts notice, which occurrence of a transmissible disease as defined in § 2 Number 3 of the infection protection law can cause , or accept, that such facts exist, must a preparation, if necessary, including a disinfecting, in accordance with generally accepted engineering standards in compliance with § 6 Paragraph 3 be done. In pipe networks or parts thereof, in which the requirements of paragraph 1 or 2 can be met only by disinfection, the entrepreneur and the other proprietor of a water supply system must according to § 3 Number 2 Letters a and b, or, if the drinking water supply is carried out as part of a commercial or public activity, to letter d or letter f a sufficient disinfection capacity by free chlorine, Chlorine dioxide or other suitable disinfectants or procedures, in accordance with § 11 are included in a list of the Federal Environment Agency, keep ready.

Clarification
The obligation to examine drinking water heating systems applies in accordance with Document drinking water regulations and legionella for drinking water installations. This is an explanation of the drinking water regulations.
- where drinking water is delivered through a public or commercial activity and
- a large plant for heating drinking water and contain
- contains the showers or other facilities, where there is a misting of drinking water.
Under the obligation to inspect fall schools and playschools as well as houses with rented out apartments or hotels, if there is a large plant is operated with hot drinking water. As large plants apply
- Water heaters with more than 400 liters content or
- water installations with one or more pipes with a volume of at least 3 liters.
Owner communities in rise condominiums of the duty to examine only have to comply, if at least one apartment is rented out in the building.
On the subject “Explosiveness of Legionella in drinking water” Many publications have been published in the special press. Here is a link to an exemplary Article in the newspaper “SBZ SANITÄR.HEIZUNG.KLIMA”.
But also on the methods used and its equipment must be paid. At least in one regulation will be rules of (economic) association declared to an act.
For the territory of the Federal Republic of Germany shall apply from the publication of the list of (…) disinfection procedures, Part II, Row 6, UV radiation (240-290 nm), Quote: There are only ultraviolet disinfection equipment permitted, for which in accordance with DVGW worksheet W 294-2 (A) as part of a biodosimetric testing disinfection efficiency of at least 400 Joule / m2 (related to 254 nm) was successfully demonstrated. The operating characteristics specified for the respective device in the test report and in the certificate of an accredited industry certifier (max. Flow and associated minimum irradiance) must be observed in operation. The disinfection method (UV) is not applicable for maintaining a disinfection capacity in the distribution network (see. § 5 Paragraph 5 Sentence 2 TrinkwV 2001).

In the field of public swimming pools
The basis of dimensioning and process selection is DIN 19643 described. The "general requirements" in Part 1 informed about the opinion of the relevant standards committee. In the normative references DIN 19643 with respect to the determination of the concentration of legionella DIN EN ISO 11731-2 and the ISO 11731 listed. About differences between the two standards is not informed.
In DIN 19643-1, Paragraph 5.3, Table 1 The microbiological requirements for the clean water (Note: water after filtering with disinfectant) and the pool water are formulated. By line 5.3.3 Legionella spec. applies the unit cfu/100ml and, split up in several footnotes,
- the upper limit of clean water (by definition filtrate plus disinfectant)
- Footnote b: In the filtrate at pool water temperature ≥ 23°C,
- Footnote c: Judgment and measures legionella findings follow 14.4 tables 7 and 8.
- The upper value for pool water
- Footnote c: Judgment and measures legionella findings follow 14.4 tables 7 and 8.
- Footnote d: In the pool water of warm spring pools and pools with additional aerosol-forming water circuits and pool water temperatures ≥23°C
The demands on the filling water and thus shifted into another table. Previously, however, pointed to at least one source of infection. DIN 19643-1, Paragraph 10.2.1: Fixed-bed filters (Sandfilters) (Quick filter): In order to avoid filter contamination of the filter ist after 13.4.2 to wash (Operating times depending on the water temperature). If this causes contamination with Legionella spec. or Pseudomonas aeruginosa can not be prevented in the long term, disinfection is required (see the recommendation of the Federal Environment Agency hygiene requirements for pools and monitoring; Anhang II).
Another clue can be found in DIN 19643-1, Paragraph 13.5 Filling water adding: (…) It should be noted, that filling water caused by stagnation and / or heating may be contaminated with Legionella.

To be in the order of the DIN 19643 to stay, the scope of investigation closes again with footnotes. According to DIN 19643-1, Table 5, Row 5.3.3, for Legionella spec. the following areas should be examined
- The filling water without further footnotes
- The filtrate
- Footnote b (for all parameters): The maximum values are shown in Tables "functional test of the filtration" in the following parts,
- Footnote c (for all parameters): During microbiological abnormalities: Follow-up of the filtrate and the pool water, Flushing filter. With new microbiological abnormalities review of the treatment, filter flushing, Follow-up of the filtrate and the pool water.
- Footnote f: In pool water temperature ≥ 23 °C.
- The clean water
- Footnote d (for all parameters): Investigations carried out only with abnormalities in the pool water and annual maintenance.
- Footnote e: Investigations must be carried out in microbiological abnormalities in the pool water. Additional examinations provide indications of a possible filter germination.
- The pool water
- Footnote g: In the pool water of hot whirlpools, and pools with additional aerosol forming water systems and pool water temperatures ≥ 23 °C.
To follow the logic applied here, it is probably not helpful. Because the temperature of the proliferation of legionella >25° C is found, is assumed, that occur throughout the cycle no higher temperatures. All other points are always based their argument on the pool water and to act: "If there something is found". Other points are not to be tested in this standard. But who does not have to look, never finds anything.
The formulations leave room too. Not everyone sees in a connected fan an additional "water cycle". But the "air line" is in the breaks with high probability not connected to the disinfectant and a good stove for Legionella. Possibly the pipeline runs in the technical room, which heat the compressor or pumps to 30 ° C. The Legionella are not temporarily stored in the pool water, but blown directly into the lungs of bathers.
The real measures are in DIN 19643-1, Table 7, Review of the pool water and measures, formulated. Depending on the result of the first investigation on Legionella following formulations are made. Less than 1 CFU/100ml done neither judgement nor measures.
From 1 to 100 CFU/100ml the assessment is "low contamination":
- On the initial examination takes place: a follow-up,
- On the follow-up takes place: follow-up, Control of the filtrate
- The further restructuring is described with: follow-up, Control of the filtrate
This is similar to a circuit. It is advisable, to include the dynamics of reproduction again in the evaluation and with the intervals between the “follow-up” to compare.
From 100 to 1000 CFU/100ml the assessment is "medium contamination":
- On the initial examination takes place: filter flushing, Check disinfectant addition, follow-up, Control of the filtrate
- On the follow-up takes place: filter flushing, Check disinfectant addition, Switch off the aerosol-producing devices, follow-up, Control of the filtrate,
- The further restructuring is described with: further measures with involving of professionals, for example superchlorination, replacement of the filter material, Switch off the aerosol-producing devices, Notification to the relevant health authority, repeated follow-up of pool water and filtrate,
More then 1000 CFU/100ml the assessment is "high contamination":
- Footnote a: In Legionella concentrations > 10 000 CFU/100 ml and legionella detection in the filtrate instant Prohibition of use.
- On the initial examination takes place: filter flushing, Check disinfectant addition, Switch off the aerosol-producing devices, follow-up, Control of the filtrate,
- On the follow-up takes place: prohibition of use, filter flushing, Check disinfectant addition, follow-up, Control of the filtrate, Released after a perfect microbiological findings in the pool water,
- The further restructuring is described with: prohibition of use, further measures with involving of professionals, from. B. Superchlorination, replacement of the filter material. repeated follow-up of pool water and filtrate, Notification to the relevant health authority, Released after a perfect microbiological findings in the pool water,
Even with positive findings 1 to 1000 CFU/100ml in the follow-up is made to the control of the filtrate in DIN 19643-1, Table 8, Judgement of the filtrate (Water after treatment before disinfectant adding) and measures, directed. Here, too, is determined
From 1 to 1000 CFU/100ml (in the filtrate) the assessment "contamination" applies:
- On the initial examination takes place: filter flushing, Follow-up of the filtrate and the pool water
- On the follow-up takes place: filter flushing, Follow-up of the treatment, Follow-up of the filtrate and the pool water
- The further restructuring is described with: further measures with involving of professionals, for example superchlorination, replacement of the filter material, Switch off the aerosol-producing devices, Notification to the relevant health authority, repeated follow-up of pool water and filtrate,
More then 1000 CFU/100ml applies (in the filtrate) the assessment "high contamination":
- On the initial examination takes place: filter flushing, filter flushing, Follow-up of the filtrate and the pool water,
- On the follow-up takes place: filter flushing, Follow-up of the treatment, Follow-up of the filtrate and the pool water, possibly usage restriction (For example, turn off aerosol-producing devices)
- The further restructuring is described with: further measures with involving of professionals, from. B. Superchlorination, replacement of the filter material, Notification to the relevant health authority follow-up of the filtrate and the pool water, possibly usage restriction,

With so frequent mention of the measure "superchlorination" must be here "Hygiene requirements for bathrooms and monitoring the recommendation of the Federal Environment Agency (UBA) after hearing the Swimming- and Pool Water Commission of the Federal Ministry of Health (BMG) at the Federal Environment Agency" and its definition of "Superchlorination" insert. In table 4 of this document are the legionella concentrations of the DIN 19643 listed. In Anhang I: Superchlorination, Paragraph 5.2 pool water, is described:
At the measure in disinfection (of the pool water) to reach disinfection capacity is characterized by a chlorine concentration of at least 10 mg/l (ppm) over a period of at least 2 h. Filter, which are coated with granular activated carbon, should, if possible, be bypassed.
In paragraph 5.3 system components, under which also filters should be considered, the chlorination is defined as follows:
The chlorine concentration should be at least 10 mg/l at a contact time of at least 2 h. When using chlorine dioxide, the minimum concentration of 1,0 mg/l ClO2 is to observe .
It should be noted, that here the infestation by Legionella is thematised. For positive legionella findings the same document says other values:
Is Legionella infestation given, then the chlorine concentration is on 50 mg/l to increase at a contact time of at least 12 h and the concentration of chlorine dioxide to 10 mg/l with a contact time of at least 24 h. (…) Are filters with grain activated carbon occupied, then the rinsing with chlorinated water is often insufficiently effective in the event of microbial contamination due to the decomposition of chlorine on the surface of the material, so that a carbon replacement is required. An attempt to superchlorination can be done, then it must be ensured, that despite the high chlorine demand in the exiting sludge water is still a significant residual chlorine concentration is present.
For the assessment of these measures "superchlorination" is important, to combine the occuring volume flows with the required concentrations.
The view of the Federal Health Ministry of Health
… about swimming- and pool water. Quotes from source:
Legal basis
The legal basis for securing and monitoring the quality of the swimming- and swimming pool water is the "Law for the Prevention and control of infectious diseases in humans (Infection Protection Act – IfSG)”.
The § 37 Paragraph 2 of the IfSG regulates the requirements for the quality of swimming- pool water in public aquaparks, Business entities and are not exclusively privately used in other entities. There it says:
"Swimming- and pool water […] must possess such properties, that by its use harm to human health, in particular by pathogens, is not to be feared".

Treatment of swimming- and pool water
The treatment of swimming- and pool water, including a disinfection, is required, to during operation of swimming- and pools - regardless, whether it is for outdoor- or indoor pools is - to be able to provide a hygienic water available to swimmers and bathers at any time. If treatment and disinfection carried out in accordance with generally accepted engineering regulations, can be assumed, that no pathogens, while bathing and swimming can be transferred. Basis for this is inter alia the DIN 19643.

New findings in the field of swimming- and pool water hygiene and the technical development of appropriate treatment methods have a revision of the standard series DIN 19643 necessitated. As a result, are now by Working Committee NA 119-04-13 AA “Swimming pool water” standards established in the NAW - DIN 19643-1 “Treatment of swimming- and pool water – Part 1: General requirements”; – DIN 19643-2 “Treatment of swimming- and pool water – Part 2: Process combinations with fixed bed- and precoat filters”; – DIN 19643-3 “Treatment of swimming- and pool water – Part 3: Process combinations with ozonation”; – DIN 19643-4 “Treatment of swimming- and pool water – Part 4: Process combinations with ultrafiltration”. The standard applies to the treatment of water, including seawater, Mineral water, healing water, Sole (and man-made) and thermal water, in swimming- and pool equipment. It does not cover the treatment of water in single-family pools and not for water in plants with biological water treatment. The aim of this document is, a good, consistent quality of the pool water in terms of hygiene, safety and aesthetics to ensure, so that damage of the human health, in particular by pathogens, is not to be feared. It is also the well-being of bathers (for example, by minimizing side reaction products of disinfection) to consider. Therefore, requirements for the water quality, the dimensioning, the operation and control will be fixed. For the processing requirements are called, by which this objective can be achieved.
But every bather can contribute, so that the water remains clean. For informations, see here.
Responsibility for the quality of swimming- pool water and monitoring
The responsibility for this lies with the relevant state authorities. The monitoring of swimming- pool water quality, including the necessary treatment plants carried out by the health authorities.
Professional relevance
Accordding to § 40 the IfSG is the Federal Environmental Agency (UBA) the task assigned, Concepts for prevention, to develop detection and prevention of the spread of communicable waterborne diseases.
The relevant work of the department "Drinking- and pooö water" of the UBA is under the supervision of the BMG. (Federal Ministry of Health)
Through the work of this department of the UBA and the relevant authorities of the countries as well as the professionals and associations concerned are supported by appropriate expertise.

Subject commission
The swimming- Pool Water Commission (BWK) is a national commission of the Federal Ministry of Health (BMG) - based at the Federal Environment Agency (UBA). She advises both authorities in the issues of swimming- pool water hygiene.
The BMG appoints together with the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety Building (BMUB) and the responsible supreme state authorities, members of the BWK for a session of three years.
The recommendations of the BWK primarily serve the public health authorities and Badbetreibern as a basis for action. The technical concepts of the UBA and the swimming- Pool Water Commission can also supply an important basis for public health strategies by federal and state governments in this area.
In the area of fountains in public spaces
In preparation!


Physical methods against Legionella
Pay attention, in particular the following texts, but generally all texts in this website, do not represent, as described in the imprint, legal advice or technical evaluation. It is exclusively the opinion of the author. The following figure illustrates the author known technical options for reducing the concentration of legionella.
Even the UV rays of the sun help as a physical method in the disinfection of water. Photo right shows the radiation during an eruption on the sun's surface.
When choosing the appropriate method following points should be considered:
- Effectiveness of the disinfection process to the target microorganism,
- Effectiveness of the disinfection process for potential hosts of the target microorganism, in the example of legionella thus the effectiveness of amoeba,
- Effectiveness of the disinfection process under the existing conditions, in the example, the turbidity of the water or the formation of the circulation,
- Necessary contact time,
- Possible disinfection by-products,
- Energy costs,
Thermal disinfection
For thousands of years humans is known, that you can water by “boiling” can make drinkable. This method is also used for supply systems.
The method is suitable for:
- Drinking water installations with circulation function,
- Process water installations with circulation function.
The method is not suitable for:
- Highly branched systems,
- Water installations without circulation function,
The following restrictions on use must be observed:
- The system must have a circulation function. This is usually available only for hot-water systems. Cold-water systems are thereby excluded.
- The materials must be heat-resistant ≥70°C.
- All parts of the pipes must be flushable. This creates the need for accessibility for the staff with at the same time inaccessible for users. For example, the showers of a sanatorium. During the thermal disinfection must be excluded, that users are affected in health by the excessively hot water.
- There should be no dead strands in the pipeline. These elements of a pipeline will be not heated, so stay as an infection stove preserved.
The benefits are:
- In the use of existing units.
Reason:
In the thermal disinfection is used, that microorganisms in high temperatures dies. For this purpose, the water of the system for a limited time is brought to a high temperature ≥70 ° C and pumped in a circuit.
Unfavorable, it is therefore, if the pipeline system of a building is not known. In the past, the use of rooms often been changed, without the pipelines adapt up to the main line. So "dead" pipe sections have been created, their water does not circulate. In these pipe sections, a hotbed of proliferation of organisms is to find.
The use of plastics for drinking water pipes has to be monitored critically. A few years ago, the Federal Environment Agency had a guideline for the hygienic assessment of organic materials in contact with drinking water (KTW-Guideline) enact.
The worksheet W551 of the DVGW rules for Thermal disinfection is described. A download or preview can not be made available here.

The district office Weilheim-Schongau advises its companies and inhabitants therefore in accordance with DVGW W551, quote https:// www.weilheim-schongau.de/:
Thermal disinfection
Thermal disinfection should cover the entire system including all abstraction fittings. At a temperature of ≥ 70 ° C Legionella are killed in a short time.
Each abstraction point is open with outlet for at least 3 minutes with at least 70°C to pressurize . Therefore, the water must be heated above 70°C in drinking water-heater. Temperature and duration must be strictly observed. The outlet temperature should be checked at each outlet.
Thus in circulation systems, the entire system (hot water- and circulation line) is covered by this measure, all outlets must be closed during the heating of the water warmer; the circulation pump must be operated in continuous operation. This operating state is maintained as long, is achieved to a temperature of 70°C in the circulation. Only after this, the abstraction fittings will thermally disinfected sequentially with opened outlet. Of course, the scald protection according to VDI 6000 and DIN EN 806 is to secure.
Depending on the size of plant and routing of pipes the thermal disinfection must be carried out section by section. In order to exclude a recontamination of the plant, the individual sections must be subjected to thermal disinfection immediately after each other. It may be necessary, interrupting the thermal disinfection, until the water-heater are heating up again.
For scalding protection during thermal disinfection is to ensure. After completion of the thermal disinfection, the system is returned to its intended use.

As so often in life, is not described here, how the realization can look practical. For this (idealized) measure must first have access to all fittings but at the same time must be excluded, that the fittings are used in this time by careless people. Children and the elderly must be considered.
UV radiation
The reproduction of the microorganisms is interrupted by irradiation with UV light. It damages the genetic. The UV radiation strikes the resonance frequencies of DNA and surface proteins of the microorganism. The DNA will be damaged, therefore, the reproduction of organisms is disturbed, but the microorganisms themselves live on. Typically, this process is called "deactivation".
By damaging or conversion of proteins often occur at a later death of the microorganisms. This seemingly trivial point plays in the comparability of examinations in the laboratory and in the Mobile Legionella Laboratory an essential role.
The method is suitable for:
- Circulatory systems,
The method is not suitable for:
- linear systems, see UBA test the effectiveness of disinfection agents 2011, Page 3: “From the water plant to the building only active substances with a disinfecting agent capacity.”
The following restrictions on use must be observed:
- The radiators reach after a few seconds the required power. The flow rate must be therefore be stopped or recycled.
- The radiators heat the water. Particularly at low flow rates, a thermal protection is necessary.
The benefits are:
- Low cost,
- Chemical free,
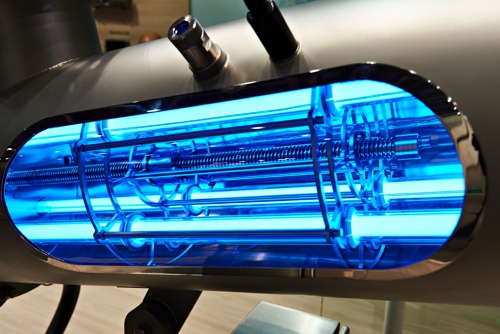
Reason:
The success of UV exposure depends on the intensity of the radiation and the attainment of the organism. It has been found, that 400 Joules/m² are sufficient, in order to prevent the most common microorganisms from multiplying. As explained in the section on infection, is not the individual Legionella for infection, but the proliferation of legionella (in the lungs) responsible. The UV irradiation is to prevent the proliferation.
In the notice of list of (…) disinfection procedures, Part II, Row 6, UV radiation (240-290 nm) is it written, Quote: (…) The disinfection method (UV) is not applicable for maintaining a disinfection capacity in the distribution network (compare § 5 Paragraph 5 Sentence 2 TrinkwV 2001).

Source: www.aqua-innovation.at
The UV irradiation is effective only at the place of installation. In each meter of pipe after the UV irradiation, the biofilm can form. Also new growing Legionella are formed in this biofilm. Therefore, a reduction of legionella concentration only in circulation systems with extremely short pipeline is to expected. The combination with chemical methods is possible and recommended.
Chemical methods against Legionella
„Insitu“ (Latin for "in place") is the opposite of "exsitu". This distinction is necessary, because the biocides either directly at the place of use (insitu) or produced in the factory (exsite) and then transported only to the place of use.
When choosing the appropriate method following points should be considered:
- Effectiveness of the disinfectant on the target microorganism,
- Effectiveness of the disinfectant to potential hosts of the target microorganism, in the example of legionella thus the effectiveness of amoeba,
- Effectiveness of the disinfectant under the existing conditions, in the example of legionella so the pH,
- Necessary contact time of the disinfectant with the microorganism,
- Possible disinfection by-products,
- Transportation risks,
- Transportation costs,
Each reader, who misses one or more good methods at this point, is cordially invited, to describe this method and transmit over the comment or an email. The decision on the publication remains with the author.

Disinfection with chlorine in situ method
The production of chlorine at the usage site is an efficient and safe method. There will be a salt for that, such as sodium chloride NaCl, split using electric energy. There arise desired chlorine Cl2 and unwanted hydrogen H2. The chlorine dissociates instantly in the pH-dependent components. The in situ process currently uses so-called tube cell electrolysis plants or membrane cell electrolysis plants.
At present there is a legal uncertainty for systems with tube cells as well as for systems with membrane cells, caused by the Biocidal Regulation. In the electrolytic reaction in a dynamic process different reaction products are formed, their variability has not considered in the biocide regulation.
The method is suitable for:
- Process water in the pH range less than pH 6.5 and,
- Water in swimming- and relaxing pools,
The method is not suitable for:
- Cooling towers, because of pH values >8,2,
- Drinking water, because of the reaction by-products,
- Disinfection of filters with active carbon layer,
The following restrictions on use must be observed:
- The chlorine can attack the materials used. The compatibility must first be ensured.
- The effectiveness of chlorine decreases with increasing pH. Therefore the use of chlorine or chlorine-containing products in applications such as in an open cooling tower is not optimal.
- When using chlorine for disinfection, disinfection by-products such as trichlorohalomethanes are formed. These products are suspected, to be carcinogenic.
- In the use of chlorine for disinfection strong smelling chloramines are formed. These also affect the taste of water.
- In the provision of chlorine from electrolytic plant are currently the uncertainties from the Biocidal Regulation.
The benefits are:
- Easy availability of industrial production,
- Possible on-site production of salts and water,
Reason:
The chlorine reacts in the dosing with the dissolved metals and organic materials in the water and generates a staining and smells, nothing else. What is left after this first reaction, applies in the next step onto the surface of the biofilm. Chlorine is probably the most widely used disinfectant for water. It kills by its strong oxidative effect on the surface of an organism. The legionella "flying" in the water or located on the surface of the biofilm are killed by the hypochlorous acid.
If amoebae be achieved through the mucus of the biofilm through, so the amoeba is only killed. The legionella inside the amoeba remain untouched. This protects the legionella. It must be used so much chlorine, that the biofilm is total killed. However, this concentration is incompatible with humans and leads to high levels of reaction by-products.

Membrane cell electrolysis plant symbolically
If the legionella should be the goal, then represents the chlorine the following problem: Legionella are a part in amoeba. The amoeba ate Legionella, but those living inside the amoeba more. The amoebae, however, are in the biofilm and are protected by its mucus.
If given chlorine for the purpose of disinfecting the water, should be a high proportion of very effective hypochlorous acid HOCl form. But this depends on the pH. Because it is a (greater) Part of hypochlorous acid in hypochlorite ion ClO– and hydrogen ion H+ split.
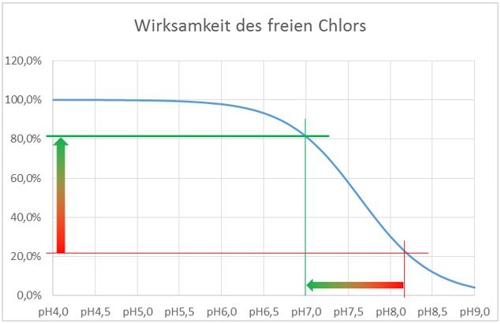
The shift from pH8.2 to pH 7.0 is illustrated by the horizontal arrow and results, that the effectiveness of 21,5% to 81,3% improved. The influence of temperature is neglected for this example.
Oxidative disinfectants can kill the amoeba. But the dead Legionella is a protection for the legionella too. Oxidative disinfecting agents such as chlorine, Ozone, H2O2 therefore have an extremely small effect. These disinfectants meet the legionella only at extremely high concentrations. For a comparison, see the Publication on filter germination.
It should also be noted, that the oxidative disinfectants have a strong dependence on the pH. For example, the use of chlorine in the alkaline water of a cooling tower does not make sense.
The only way it is therefore, to change the pH-value or to live with a reduced activity.
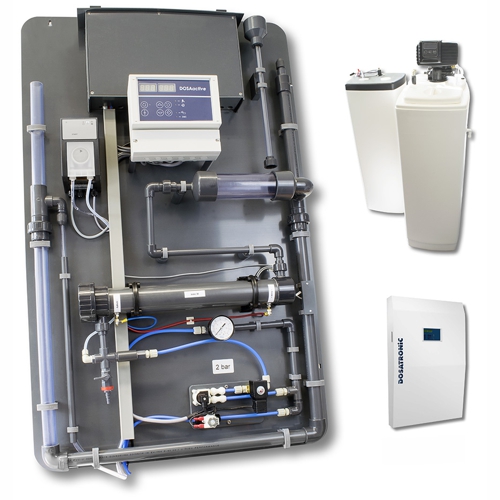

Disinfection with chlorine in the ex situ method
The following description applies currently for the use of non-at-produced chlorine in the standardized DIN delivery.
- Liquid sodium hypochlorite according to DIN EN 901,
- Solid calcium hypochlorite according to DIN EN 900,
- Chlorine gas, liquefied, according to DIN 19607,
The description does not apply:
- Trichlorisocyanuric acid, including as tablets.
The method is suitable for:
- Process water in the pH range less than pH 6.5 and
- Water in swimming- and relaxing pools,
The method is not suitable for:
- Cooling towers, because of pH values >8,2 and
- Drinking water, because of the reaction by-products,
- Disinfection of filters with active carbon layer,
The following restrictions on use must be observed:
- The chlorine can attack the materials used. The compatibility must first be ensured.
- The effectiveness of chlorine decreases with increasing pH. Therefore the use of chlorine or chlorine-containing products in applications such as in an open cooling tower is not optimal.
- When using chlorine for disinfection, disinfection by-products such as trichlorohalomethanes are formed. These products are suspected, to be carcinogenic.
- In the use of chlorine for disinfection strong smelling chloramines are formed. These also affect the taste of water.
- In the provision of chlorine from electrolytic plant are currently the uncertainties from the Biocidal Regulation.
The benefits are:
- Easy availability of industrial production,
Reason:
The chlorine reacts in the dosing with the dissolved metals and organic materials in the water and generates a staining and smells, nothing else. What is left after this first reaction, applies in the next step onto the surface of the biofilm. Chlorine is probably the most widely used disinfectant for water. It kills by its strong oxidative effect on the surface of an organism. The legionella "flying" in the water or located on the surface of the biofilm are killed by the hypochlorous acid.
If amoebae be achieved through the mucus of the biofilm through, so the amoeba is only killed. The legionella inside the amoeba remain untouched. This protects the legionella. It must be used so much chlorine, that the biofilm is total killed. However, this concentration is incompatible with humans and leads to high levels of reaction by-products.

If the legionella should be the goal, then represents the chlorine the following problem: Legionella are a part in amoeba. The amoeba ate Legionella, but those living inside the amoeba more. The amoebae, however, are in the biofilm and are protected by its mucus.
If given chlorine for the purpose of disinfecting the water, should be a high proportion of very effective hypochlorous acid HOCl form. But this depends on the pH. Because it is a (greater) Part of hypochlorous acid in hypochlorite ion ClO– and hydrogen ion H+ split.

The shift from pH8.2 to pH 7.0 is illustrated by the horizontal arrow and results, that the effectiveness of 21,5% to 81,3% improved. The influence of temperature is neglected for this example.
Oxidative disinfectants can kill the amoeba. But the dead Legionella is a protection for the legionella too. Oxidative disinfecting agents such as chlorine, Ozone, H2O2 therefore have an extremely small effect. These disinfectants meet the legionella only at extremely high concentrations. For a comparison, see the Publication on filter germination.
It should also be noted, that the oxidative disinfectants have a strong dependence on the pH. For example, the use of chlorine in the alkaline water of a cooling tower does not make sense.
The only way it is therefore, to change the pH-value or to live with a reduced activity.
Disinfection with chlorine dioxide in situ method
Chlorine dioxide is used worldwide as a disinfectant and more important. This success is built:
- by the toxic effects on organisms,
- the high degree of independence from the pH of the water and
- the difference of the reaction by-products of chlorine dioxide to the reaction by-products of chlorine.
A detailed justification for the use of chlorine dioxide is in the newspaper article to Biological contamination of the filters to read about legionella. The topic “Situ production” is already in Tutorial chlorine dioxide generator discussed in detail.
Details for dimensioning, for safety, for consumption and downloadable tables for own calculation are Tutorial chlorine dioxide generator also included.
The following presentation is an example of one of the operating modes. Clicking in the window of the presentation start a production cycle. Other operations are in Tutorial chlorine dioxide generator shown.

The method is suitable for:
- Cooling tower systems,
- Drinking water systems,
- Process water systems,
- Disinfection of filters with active carbon layer,
The method is not suitable for:
- swimming- and relaxing pools, because of the eventual thickening of chlorates
The following restrictions on use must be observed:
- For use in drinking water, the volume flow-proportional dosing is required by the DVGW. This requirement excludes, that errors in the measurement lead to a harmful overdose. Nevertheless, the measurement and archiving of the concentration of chlorine dioxide is recommended.
- A high concentration of chlorine dioxide in water can lead to an explosive gas phase.
- The transportation of chlorine dioxide is not permitted in many states.
- The dosage of chlorine dioxide can lead to the formation of chlorates. This Chlorate can be toxic to humans. In circuits, this Chlorate can focus over time.
The benefits are:
- Efficacy in a wide pH range,
- Toxic effect to microorganism,
- The exclusive transport of sodium NaClO2 and hydrochloric acid HCl,
- Missing more reaction byproducts,

Reason:
Chlorine dioxide in addition to the oxidative effect also has a toxic effect. The toxic effect is based on the destruction of cell membranes. Therefore, not only the amoebae but also the legionella protected in the amoebae are reached.
With chlorine dioxide, it is possible, reduce the biofilm and to keep permanently removed.
Also chlorine dioxide is partially used also by the dissolved metals. But the rest exerts a toxic effect on the organisms. The cell walls are penetrated. Because the chlorine dioxide ClO2 but only very small reacts with the organic compounds, there are no organic reaction byproducts, such as THM or AOX. Chlorine dioxide breaks the molecular bonds in the cell and at the same time changed the protein structure, so that the cells can not convert it into resistant forms. A development of resistance of germs is thus effectively prevented.
Chlorine dioxide has been used successfully for the disinfection of drinking water in waterworks since the mid-50s and has already several times the name of related chlorine, but which may form harmful reaction byproducts, replaced.
This tutorial provides a detailed description for chlorine dioxide generators.
Disinfection with chlorine dioxide in the ex situ method
For completeness, it should be mentioned, that there are manufacturers, who promote the supply of "stabilized chlorine dioxide". The number of suppliers has decreased in recent years.
Alone the possibility, to transport chlorine dioxide, is already in conflict with the restrictions and safety rules previously described. See tutorial chlorine dioxide generator section Security.
Explained by one manufacturer, Quote:
(The product) is a patented, ready for use and stabilized ClO2 – solution. It eliminates excellent in all areas of water occurring microorganisms (germs, bacteria, algae and legionella). The extra-strong active content of 10% the product is particularly suitable for the continuous degradation of biofilm and its prophylactic treatment. The product in addition to the product features listed below, it still has some significant advantages over, for example. Chlorine dioxide generator plants. In addition to the significantly lower cost of a metering system, our product is neither explosive nor flammable and the application area is not tied to a fixed location. Because the high active share 10% is the product highly effective even in low concentrations.
Product features
- inorganic liquid ClO2 (stabilized chlorine dioxide)
- immediate ready for use at the factory; the preparation of a solution on site is eliminated
- up to 6 Month storable
- extremely high active ingredient content of 109g/l (10 %solution)
- one of the strongest disinfectant products for water worldwide
- safe elimination of microorganisms, such as germs, bacteria, Legionella etc..
- Reduction of biofilm formation and protection against
- Removal of iron, Manganese and other metals
- Reduction of organic compounds (THM)
- Increase of the redox potential by high oxidation potential
- lower AOX compared to other disinfectants- / Oxidation products
- The product is free of chlorite
- Microorganisms can not become resistant to the product develop
- Approved for water treatment in the food- and beverage industry
- easy and safe application – non-flammable / non-explosive
It should again be pointed out at this point, that according to the general rules of chemistry, the gas via a liquid chlorine dioxide with the concentration >8g/l will be explosive. As already written above, see the Security section in the tutorial to chlorine dioxide generators. This manufacturer is reported as active "chlorine dioxide" and in point 4 of the previous list, an active substance content of 109g/l listed.

The data sheet for the same (!) Product can be read, Quote:
The individual reactions of (…) oxygen attaches to the reaction partner. Reducing anions such as sulfite, nitrite, etc.. be converted directly into the maximum value oxidative. Organic compounds can be converted either into oxygen derivatives, or in carboxylic acids, depending on the composition and structure, which further hydrolyze depending on the pH value in carbon dioxide and water. The biocidal effect resulting from the shift of the redox potential of the with (…) treated water and by oxidative disruption of protein structure syntheses, whereby development of resistance of microorganisms are excluded. The algicidal effect results from the oxidation of chlorophyll. The product works against pathogenic and non-pathogenic bacteria, yeasts, algae and viruses.
Some numbers of the manufacturer's information cited here allow the conclusion, that this described product works on chlorine basis. Therefore, the following properties are taken from the properties of disinfection with chlorine in the ex-situ method, and repeated.
The method is suitable for:
- Process water in the pH range less than pH 6.5 and
- Water in swimming- and relaxing pools,
The method is not suitable for:
- Cooling towers, because of pH values >8,2 and
- Drinking water, because of the reaction by-products,
- Disinfection of filters with active carbon layer,
The following restrictions on use must be observed:
- The chlorine can attack the materials used. The compatibility must first be ensured.
- The effectiveness of chlorine decreases with increasing pH. Therefore the use of chlorine or chlorine-containing products in applications such as in an open cooling tower is not optimal.
- When using chlorine for disinfection, disinfection by-products such as trichlorohalomethanes are formed. These products are suspected, to be carcinogenic.
- In the use of chlorine for disinfection strong smelling chloramines are formed. These also affect the taste of water.
- In the supply of a disinfectant without specific mention of the biocidal shares must currently uncertainties from the Biocidal Regulation be assumed.
Reason:
Stated in the introduction.
Biological methods against Legionella
Probiotic displacement
The concept of probiotic displacement follows the approach: WITH microorganisms living instead of believing, that you can destroy them. One should be aware of: Bacteria belong to humans!
In the case of the probiotic displacement (from nature) selected bacteria will be used, to displace undesirable microorganisms. This is not a disinfection process and therefore can not be used in combination with disinfectants.
The microbial community makes through its own dynamics for displacement. Is the biofilm in equilibrium, the vacancies are filled through you probiotic bacteria. These may be the places of the safety margin. But it can also be places, which made free with a conventional chemical disinfection. The probiotics do not kill or replace other microorganisms, there are only good microorganisms from probiotics added. Due to the natural regeneration of microorganisms, bad bacteria are slowly but surely displaced by probiotic bacteria.
The method is suitable for:
- Open and closed cooling circuits,
- Surface treatment,
- Fish breeding,
The method is not suitable for:
- public swimming- and relaxing pools,
- Drinking water supply systems, because legal gaps (still) are not closed,
The following restrictions on use must be observed:
- Not compatible with disinfectants,
- No effect on insects and small animals,
The benefits are:
- ecological process
Reason:
Disinfection tears a hole in the composite of organisms. The species with the fastest increase fill this gap and move so that the balance in their favor. The art of dosage of probiotic bacteria is, to fill these gaps with a probiotic species to shift the equilibrium to the detriment of Legionella.
Since this is not a "acknowledged rule of technology", there are no rules, that do not prohibit or regulate this type of water treatment, or allow them. In this vacuum, it needs confidence and a quick way of checking the results. A realistic implementation is only possible using fast examination methods, as for example from Mobile Legionella Laboratory.
In a detailed Tutorial for probiotic displacement the function is described.
Historical development of biological water treatment
Essential inventions have been made in the history of human evolution, been lost again and re-evaluated. Of course, a person could, who nothing knew of the existence of microorganisms, do not judge their effect correctly. But the human could observe the effect often and learn to master by imitating.
It is now known, that there are at almost any place on earth microorganisms, that change the water in their area. Is generally understood by the term “watertreatment” a targeted influence on water quality, by whomever.
Biological treatment processes find their role models in nature and are therefore much older than the "chemical inventions" of the people. In the Middle Ages, people had recognized, that drinking beer can be more digestible than drinking water from the polluted environment. The brewer's yeasts used probably have converted more than hops and malt.
Today, the same or similar processes in natural waters are held in the biological water treatment often. The many biological wastewater treatment plants are a testament to the benefits of biological water treatment. Biologically intact water and the organisms that occur in it have the ability, nutrient inputs and anthropogenic, created by humans, loads to take and convert.

It is known, that microorganisms displace some bacteria, ferment organic material and thereby reduce harmful substances. This can of course not be generalized and requires the reduction of legionella very specific measures.
… and who does not recognize it, Microorganisms work here in attraction of being biological treatment plant:

Proof of effect
A colony forming unit (KBE) is a parameter, which plays a role in the quantification of microorganisms, namely when the viable cell count of microorganisms in a material is determined culturally.
Microorganisms can be quantified among other cultural methods, for example, a surface-viable count or a plaque assay. In this case, usually a sample of the material, whose microorganisms content is to be determined, distributed as evenly as possible on the surface of a culture medium-gel or gel in the culture medium, so that in the ideal case all individuals of the microorganisms individually and far enough from each other come to rest and form under suitable culture conditions by growth and propagation each one visible to the eye colony.
A microorganism culture produced by the cultivation of microorganisms. Meanwhile, the organisms grow by cell division in a suitable culture medium under controlled conditions, among other things, a certain temperature and the presence or absence of oxygen. Using a microorganism culture the organism type can be more closely examined. Thus, a culture of bacteria can for example be isolated from a sample, in order to detect the bacteria contained therein.
As a disinfectant the reduction of microorganisms is by definition to 10-5 KBE. If 1.000.000 CFU were present, then already holds a remnant of 100 KBE "sanitized" as.
The detection of Legionella is according to ISO 11731 performed. However, this standard allows great leeway in carrying out analysis, so different labs also get different results. Therefore, it was in Germany, but only for drinking water and swimming pool water, the DIN EN ISO 11731 Part 2 developed and fixed. Within this method 2 Series of examinations carried out. Series 1 operates on a direct approach on a GVPC (Gas Vesicle Protein C) and series 2 operates through a membrane filtration with cellulose nitrate.
Both approaches 10 days developed at 36 ° C in the incubator and 3-times controlled. If cultures are developed, a retest on cysteine agar ground within a further 2 days incubated. The detection methods say, that all colonies, growing on agar GVPC, but show no growth on cysteine-free medium, as Legionella spp. to be viewed as.

The samples are detected practically in parallel in different dilutions carried out so that a counting all areas. An elaborate process.
Ultimately, the proof of the effectiveness of all measures against Legionella is only on the Prior-After Comparison.
No matter what rule you put as basis, for example the Drinking Water Regulation, there is always the "sharp" cut-offs 10², 10³, 104 (according to the filter Recommendation of the Federal Environment Agency) and 106KBE.
A presentation of the Federal Environment Agency “Examination the effectiveness of disinfectants” gives an insight into the training of the Public Health Service on this topic. Annotation: Note, that in the presentation, the encapsulation of Legionella in amoeba was not considered apparently.
At the end is the question, the purpose for which the investigation is made. Is it for the scrutiny of authorities, then must be adhered strictly to the norm. But is it for self-monitoring, Optimization or risk minimization, then that offers itself Mobile Legionella Laboratory to you. With this tool, the errors are minimized.
Uncertainties in the sampling
Sampling for microbiological examination can always provide only a snapshot. Even if the applicable standard DIN EN ISO 19458 is fully respected for sampling, there are systemic uncertainty. In least cases, Legionella are homogeneously distributed in the water, because they are mostly embedded in the biofilm. It is thus an example of a sample of 1 liters in volume of 100m³ exist following theoretical possibilities:
- The sample contains no single Legionella,
- because the sample exactly 0,001% the water volume taken from, that does not contain "free-flying" Legionella or
- because the water speed during the trial was so low, that the biofilm nothing could be swept away.
- The sample contains a few single Legionella,
- because the Legionella are common and relatively homogeneously distributed or
- because the sample was taken at the right time in the right place.
- The sample contains a large amount of Legionella,
- because the Legionella are very common and present homogeneously or
- because you (the) one "pregnant" amoeba up to 800 Legionella has in the sample.
The sample taker has no influence on these factors. The concentration in the sample is thus highly dependent of random. Nevertheless applies: Sampling is the key process for the provision of representative samples.

Against this background, the following definition should be considered. VDI 2047 sheet 29.2 risk assessment: To carry out regular hygienic-microbiological tests during operation, representative sampling points must be defined throughout the entire system.
Uncertainties during transport
Using the example of ex situ method for chlorine dioxide can be shown, how important it is, to have been as a sampler of all information about the existing disinfectants. VDI 2047 sheet 29.3.2.1 Regular laboratory tests: The sampling sample containers have to be used, containing a neutralizing medium, at least for oxidative biocides (as example sodium thiosulfate). Since not all biocides used in practice by neutralization media in accordance with DIN EN 13623, Attachment B, can be inactivated (not oxidative biocides), are additional rules to be observed during sampling. The laboratory and the sampler is for selecting the neutralizing medium before sampling the type of biocide (Safety Data Sheet) to announce.
The sampler has generally also responsible for the transport to the laboratory. As shown in section "Dynamics of multiplication", Legionella proliferate at temperatures:
- 5 – 20 °C standstill,
- 20 – 25 °C slow replication

If it comes to samples from a hot-water system or from a cooling system, then these samples also have an optimum temperature for the proliferation of Legionella. It is therefore necessary, the samples to cooled to below 20°C immediately. For this, the sampler must be equipped.
This temperature <20°C must be maintained on the entire transport.
Uncertainty when evaluating
For the laboratory method
Quote Veolia, Challenge Legionella, Basics, risks, Preventing and combating, Dr. Hartmut Lausch, 2016:
Legionella have very specific nutritional requirements and are therefore not be cultivated on conventional culture media. Accordingly, they are not detected also in determining the number of colonies (CFU) after drinking water regulations. For this parameter (Colony forming units) can therefore no statements about a possible Legionella infection derived.
Because of the pathogenicity of Legionella only investigation laboratories are approved for analytical detection, have the permission to §44 IfSG. (because the cultivation in CFU requires a targeted multiplication of the Legionella)
If several of such laboratories with the analysis of the same sample commissioned, will too, if shortcomings in sampling and transport / storage by complying with the DIN EN ISO 194583 may be excluded, obtained sometimes very divergent analysis results.
One reason for this is to be seen in it, that no general standardized procedure for the Legionella analysis exists in Germany. Just as in many other countries has been and will be based on the international standard ISO 11731 and resorted. Since this standard allows many possibilities for variation in the analysis, the distribution of analysis results obtained in this way is correspondingly high for this reason alone.
Therefore, it was in Germany - but only for the indication drinking- and swimming pool water – developed a special protocol, tested in a ring trial and as DIN EN ISO 11731 Part 2 enshrined.
(…)

But even with this – compared to the international standard – quite restrictive procedure, show the ring tests, which according to the recommendations of the Federal Environmental Agency. the DIN the Lower Saxony State Health Department, location Aurich, on behalf of the Lower Saxony Ministry of Social Affairs, women, family, health and integration performs twice a year with Legionella, a very large variation of the laboratories involved in each several hundred received analytical results.
(…)
With this strong fluctuation range up to a factor of 30 and more the uncertainty is connected, that is behind a for the cooling tower operation quite rule-compliant Legionella findings of 500 CFU/100ml with a fluctuation range by a factor 20 with 10.000 CFU/ml limit values are exceeded by 10 times or even a result of only 25 CFU/100ml could conceal, which would not even reached the technical measure value of Drinking Water Regulation.
Evaluation using the Mobile Legionella Laboratory
Description and qualitative function:
- The living, active, effective Legionella be genetically "captured" and coupled to magnetic micro-bits. Legionella are separated by means of magnets, and rinses in several steps.
- By color tracer are made the bacteria visible.
- The number of Legionella is detected and then displayed photometrically.
- The sequence comprises a plurality of process steps. These steps take a total of about. 60 minutes. You can edit multiple samples simultaneously. While working full manual in Kit A, is offered in the kit B is a partially automated solution with a vacuum pump and an agitator.
Quantitative results:
- In analysis of a sample of 1000 ml is an accuracy of 60 … 106 KBE / CFU achieved per 1000ml.
- This corresponds to an accuracy of 6 CFU/100ml.
- Higher accuracies can be achieved by increasing the sample.
Disadvantage:
- This method is (still) not recognized by German authorities as a substitute of a laboratory measurement across cultures according to DIN EN ISO.
Advantages:
- Measurement results are immediately, after about. 60 minutes, available. The 10-day growing the cultures in an incubator is eliminated.
- The reaction rate for any exceedances and the leeway between institutional controls are considerably larger.
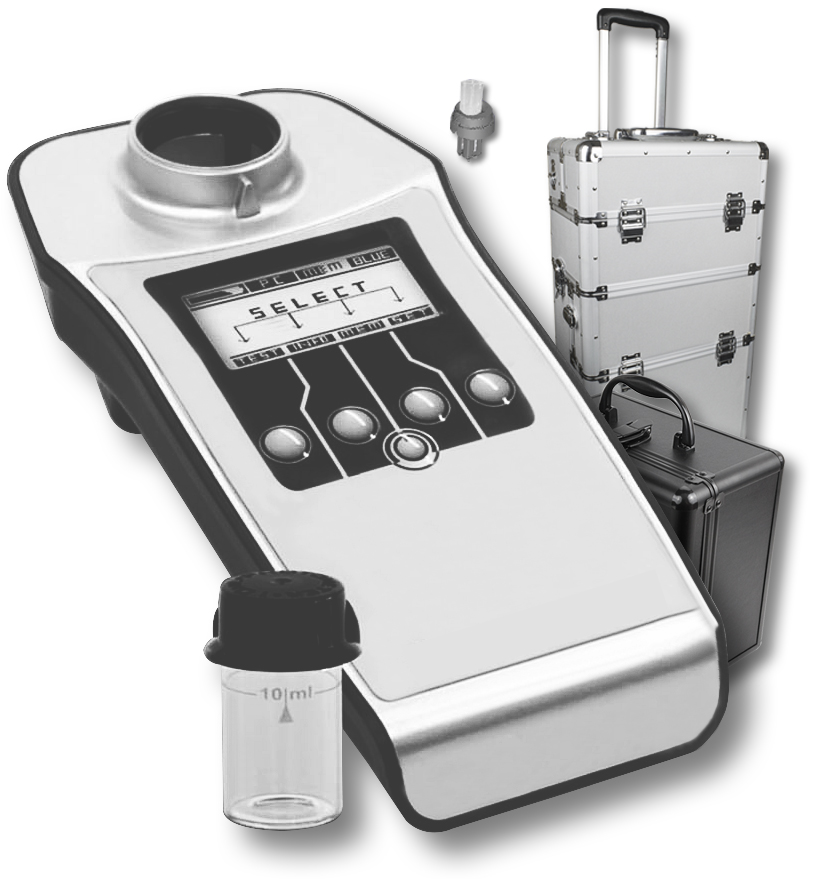

- The measurement can be made on site. As a result, distortions caused by transport, which is limited by standards at 24h, and a lack of cooling are impossible.
- Compared to the PCR method, the false positive results are avoided by already killed Legionella. Only living Legionella will be detected.
- Compared to the cultivation, better results are achieved, as well as so-called “not cultivable subspecies” Legionella are detected.
- The test can be carried out with its own trained personnel, that's why:
- Successful use on cruise ships of Carnival Cruise Lines.
- The American AOAC certification is available and has been validated by EMLabs in Philadelphia.
The complete description and all details about Mobile Legionella Laboratory available here.
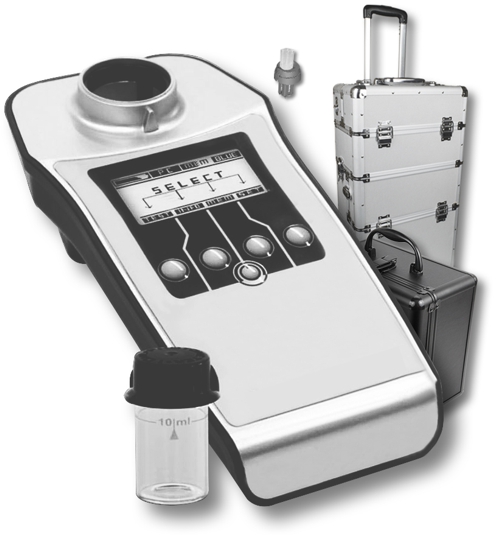





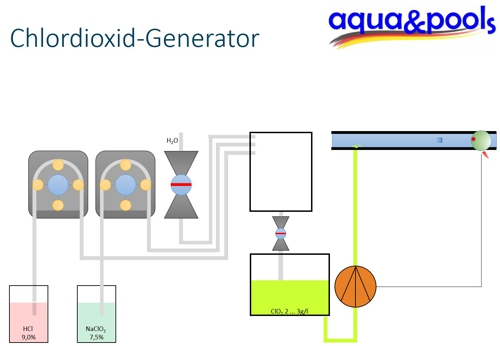


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.