


If we talk about disinfection, then most people immediately think of "chlorine". Here is often overlooked, that chlorine in different forms occurs. While the right eye can be protected by "free chlorine" for infections, is the left eye may be the result of bounded chlorine and his children in the air. This bound chlorine is the reason for the bad taste and smell in the air - but has very little to do with the disinfection or our protection. Membrane-covered sensors can also detect this kind of chlorines.
As usual in life, it is very beneficial, to measureall all parameters of a process online and accurately . Not enough disinfectant can endanger the health or in the industry production. With too much disinfectant, people can be endangered as well, but more often are financial losses caused by overdose. Reliable system with membrane-covered amperometric sensors are recognized by the German authorities in public swimming pools and are distributed worldwide.
Effectiveness
Even Free Chlorine comes in different forms, even simultaneously, out. The composition depends on the pH value of the water. The membranes and electrolytes allow the measurement in different pH values, perhaps even in moving pH values. In cooperation with a controller such as the DCW 400IP the membrane-covered amperometric sensors can even make a statement on the effectiveness of the free chlorine in the current environment.
Many disinfectants, many variations
Already described the subgroups of chlorine. But this is only the first impression amperometric of the possible variability of the membrane-covered sensors. The free chlorine can also be attached to isocyanuric acid, which membrane-free measurement disturbs. Likewise, the absence of disinfectants for some processes is necessary. At some plants, the delicate membranes of the filter must be secured. But the world of disinfectant does not end with chlorine. It is possible to measure:
- Chlorine
- Bromine
- Chlorine dioxide
- Ozone
- chlorites
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Peracetic acid
Use without controller
Membrane-covered amperometric sensors are also equipped with a recording of the current temperature of the liquid and already consider this internally. So these sensors are also without a special regulator anywhere in the world, in combination with solar systems too, usable.
The following signals can be transmitted to the environment:
- 0 … -2000mV,
- 4 ... 20mA,
- ModBus RTU,
Easy maintenance
With correct use of the membrane-covered amperometric sensors whose life is infinite. Only the electrolyte and the membrane cap should be changed regularly.


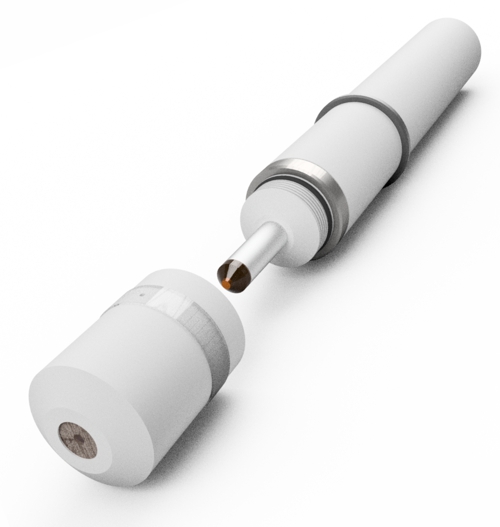
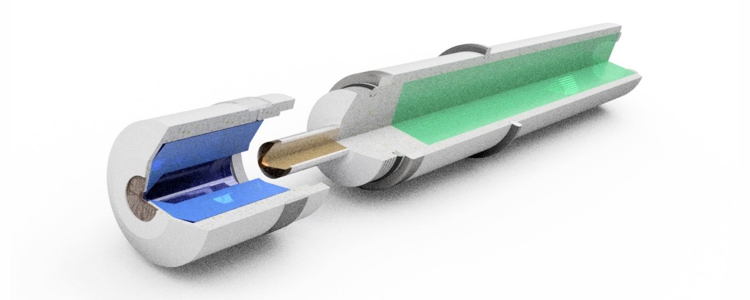
The membrane mainly allows molecules of the desired disinfectant to pass through. This possibility of selection is not possible without membrane. Without membrane, the electrolyte can not exercise some of its function, to buffer the pH-value, or to select further between individual disinfectants. The important working electrode is also exposed to the contamination of the water, which making sometimes necessary cleaning devices or cleaning by electrical circuits.
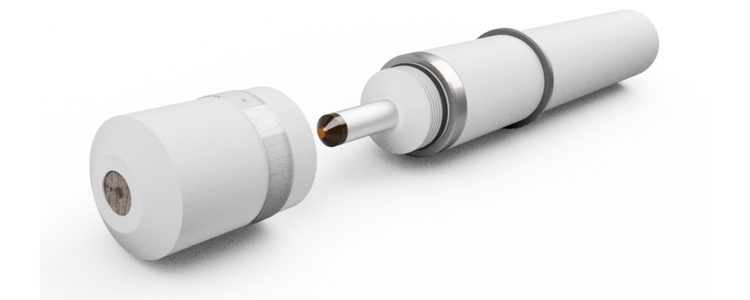
Sensors without membrane are less pressure sensitive. WIth the sensors of the type DOSASens AS no specially suitable electronics in the signal transmitter is required. An example of the DOSASens AS in the picture above.
Simple electrodes with one or more surfaces of a precious metal, usually gold or platinum, always need a special controller. The compensation of the temperature must be present in the controller. Standard signals can not be output from the sensors. An example of a sensor without own electronics in the lower picture.

The advantages of the membrane and of the electrolyte are not offered by the copper-platinum sensor. He does not have both. To measure a disinfectant, the "amperometric" principle requires a very precise electrical voltage between the reference electrode and the working electrode. In the membrane-covered sensor, this voltage is directly supplied from the electronics and adjusted very precisely.
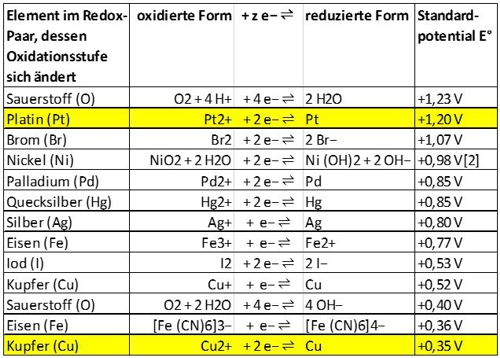
In the copper-platinum sensor, the natural potential difference between the metals copper and platinum is used. The natural voltage is in addition the size of the surfaces, water flow rate and the oxidation state of the copper depending. Typically, the copper surface is bombarded with small glass balls to remain oxide-free.
All together leads to a voltage, which can not be accurately assigned to the disinfectant. The electric currents, flowing between copper and platinum, are therefore very small and require complex processing. The copper-platinum sensor can not be used without special transmitter.

The DPD method is mainly implemented as manual measurement by means of a photometer or by a visual color comparison. But continuous measurements are available. This method does not allow, to distinguish between disinfectants, because in the result always the same color is measured or compared. The manual handling leads to large individual errors. The result can be influenced by the measured person. The method is used for most of the parameters as a source of reference values of the "calibration" of the transmitter. (Here you will find an extensive multi-part tutorial to calibrate the transmitter.)
The DPD measurement is a patented method, wherein the effect of the disinfectant is used on a dye. The dye is dipropyl-p-phenylenediamine. About conversion factors and additional substances, the DPD method is adapted to the suspected disinfectants. To adapt the same knowledge about the process but are necessary, as described for the selection of sensors.
Already in the picture on the left the color scale are two important points to see. In the upper label is visible, that the measurement can not distinguish between chlorine on the left side and bromine on the right side. If, as is common at least in Germany and Austria, The free chlorine under a limit of 0,3 to 0,6 Milligrams per liter to be maintained, this will not succeed with the gradation of colors.

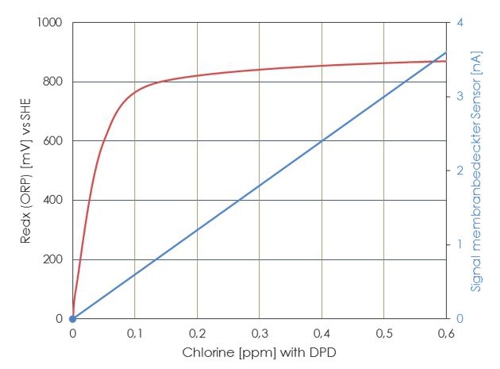
The oxidation-reduction potential or short ORP is the measurement of the assets of the water, to pick up or release electrons from a chemical reaction. In this case, an oxidation causes the release of electrons, the reduction a gain of electrons. The ORP of the water can thus be changed by adding chemicals, if they are reductively or oxidatively effective.
However, the ORP is also subject to other factors, such as temperature, Ionic strength and pH. The formation of the ORP is not limited to the known disinfectants, it can also be affected by further chemical reactants. It could be argued:
Σ(Cl2, ClO2, O3, Fe3+, Cl– , O2, …)
Even if optimal conditions prevail and no unwanted reactants are present, the ratio of disinfectant concentration and redox potential is not linear. The straight line in the diagram shows the course of the current strength to a membrane-covered amperometric sensor, the curve derived from a ORP electrode. Particularly in the control range between 600 and 800 Millivolt a transmitter can not evaluate actual values for the concentration of a disinfectant.
Often only the limit values are used. If the ORP is less than 700mV then the controller is dosing , if 750mV are achieved, then stops the controller. In conjunction with the relatively long reaction time of the sensor one could have the impression, to reach a constant concentration of the disinfectant. This impression is a fake.

The nose is deceptive! Because chlorine is odorless! But not in connection with urea. How aquaparks regulate the handling of chlorine. And should pay attention visitors to which .
Who is disgusted easily, please do not continue reading now: If it smells of chlorine in the pool much, this means NOT, it's very clean there - on the contrary: The chlorine is odorless. Only in conjunction with other substances, the chlorine gets its typical smell: Urea. The first association is: Urine in the water. Where it all comes forth? How much is in there? And how do you get it out again? Is the chemical compound of urea and chlorine harmful?
If people visiting the swimming pool, land dander, sweat, makeup and urine in the water. The disinfectant is to make these substances harmless, it combines with these substances, and it gives the typical swimming pool smell. The nose therefore does not take the concentration of the disinfectant was, the nose decreases the concentration of harmful byproducts was.





Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.